1. ArrayList集合底层数据结构
ArrayList集合介绍
List 接口的可调整大小的数组实现。
数组:一旦初始化长度就不可以发生改变
数组结构介绍
增删慢:每次删除元素,都需要更改数组长度、拷贝以及移动元素位置。
查询快:由于数组在内存中是一块连续空间,因此可以根据地址+索引的方式快速获取对应位置上的元素。
2. ArrayList继承关系 2.1 Serializable标记性接口
介绍 类的序列化由实现java.io.Serializable接口的类启用。 不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反 序列化。 可序列化类的所有子类型都是可序列化的。 序列化接口没有方法或字段,仅用于标识可串行化的语 义。
序列化:将对象的数据写入到文件(写对象)
反序列化:将文件中对象的数据读取出来(读对象) 2. Serializable源码介绍
Serializable源码介绍
1 2 public interface Serializable { }
案例: 通过序列化流序列化和反序列化集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import java.io.Serializable;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student implements Serializable { private String name; private Integer age; @Override public String toString () { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append("Student{name='" ); sb.append(this .name); sb.append("', age=" ); sb.append(this .age); sb.append("}" ); return sb.toString(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.heima.serDemo.demo;import com.heima.serDemo.domain.Student;import java.io.*;import java.util.ArrayList;public class SerTest02 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Student s1 = new Student ("悔创阿里杰克马" ,51 ); Student s2 = new Student ("会打一点长几颗" ,26 ); Student s3 = new Student ("容颜老去蒋青青" ,32 ); Student s4 = new Student ("将里最丑刘一飞" ,27 ); ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList <Student>(); list.add(s1); list.add(s2); list.add(s3); list.add(s4); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("Test\\stu.txt" )); oos.writeObject(list); oos.close(); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("Test\\stu.txt" )); ArrayList<Student> list1 = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject(); for (Student student : list1) { System.out.println(student); } } }
2.2 Cloneable 标记性接口
介绍 一个类实现 Cloneable 接口来指示 Object.clone() 方法,该方法对于该类的实例进行字段的复制是合 法的。在不实现 Cloneable 接口的实例上调用对象的克隆方法会导致异常 CloneNotSupportedException 被抛 出。简言之:克隆就是依据已经有的数据,创造一份新的完全一样的数据拷贝 Cloneable源码介绍
1 2 public interface Cloneable { }
克隆的前提条件
被克隆对象所在的类必须实现 Cloneable 接口
必须重写 clone 方法
clone的基本使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package com.heima.cloneDemo.demo;import java.util.ArrayList;public class ArrayList_Clone { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("人生就是旅途" ); list.add("也许终点和起点会重合" ); list.add("但是一开始就站在起点等待终点" ); list.add("那么其中就没有美丽的沿途风景和令人难忘的过往" ); Object o = list.clone(); System.out.println(o == list); System.out.println(o); System.out.println(list); } } 输出 false [人生就是旅途, 也许终点和起点会重合, 但是一开始就站在起点等待终点, 那么其中就没有美丽的沿途风景和令人难忘的过往] [人生就是旅途, 也许终点和起点会重合, 但是一开始就站在起点等待终点, 那么其中就没有美丽的沿途风景和令人难忘的过往]
clone源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object clone () { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super .clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0 ; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError (e); } }
案例:已知 A 对象的姓名为豹子头林冲,年龄30 。由于项目特殊要求需要将该对象的数据复制另外一个对象 B 中,并且此后 A 和 B 两个对象的数据不会相互影响
案例:已知 A 对象的姓名为鲁智深,年龄30,技能为倒拔垂杨柳 (技能为一个引用数据类型 Skill ),由于项目 特殊要求需要将该对象的数据复制另外一个对象 B 中,并且此后 A 和 B 两个对象的数据不会相互影响
方式一:创建两个对象模拟
准备学生类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package com.heima.cloneDemo.domain;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student implements Cloneable { private String name; private int age; }
准备测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class CloneTest01 { public static void main (String[] args) { Student stu1 = new Student ("豹子头林冲" ,30 ); Student stu2 = new Student (); stu2.setName(stu1.getName()); stu2.setAge(stu1.getAge()); System.out.println(stu1 == stu2); System.out.println(stu1); System.out.println(stu2); System.out.println("----此时不管修改哪个对象的内容,stu1和stu2都不会受到影响----" ); stu1.setName("扈三娘" ); System.out.println(stu1); System.out.println(stu2); }
控制台效果
false Student{name=’豹子头林冲’, age=29} Student{name=’豹子头林冲’, age=29} —-此时不管修改哪 个对象的内容,stu1和stu2都不会受到影响—- Student{name=’扈三娘’, age=29} Student{name=’豹子 头林冲’, age=29}
方式二:使用克隆
1.定义Javabean类
学生技能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Skill implements Cloneable { private String skillName; @Override protected Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super .clone(); } }
学生类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package com.heima.cloneDemo.domain;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student implements Cloneable { private String name; private int age; private Skill skill; @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super .clone(); } }
2.定义测试类
测试类
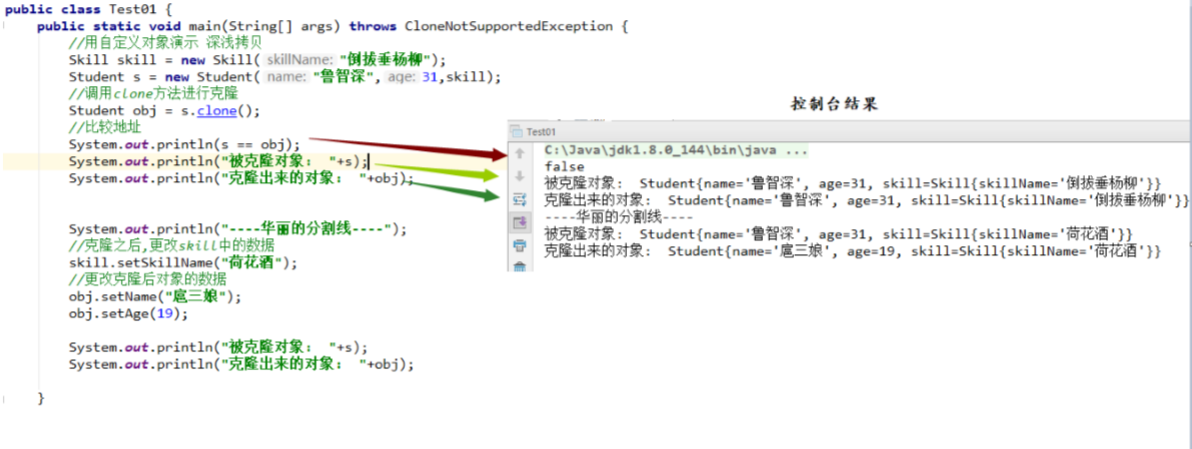
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { Skill skill = new Skill ("倒拔垂杨柳" ); Student s = new Student ("鲁智深" ,31 ,skill); Student obj = s.clone(); System.out.println(s == obj); System.out.println("被克隆对象: " +s); System.out.println("----华丽的分割线----" ); skill.setSkillName("荷花酒" ); obj.setName("扈三娘" ); obj.setAge(19 ); System.out.println("被克隆对象: " +s); System.out.println("克隆出来的对象: " +obj); } }
控制台效果
存在的问题 : 基本数据类型可以达到完全复制,引用数据类型则不可以
原因 : 在学生对象s被克隆的时候,其属性skill(引用数据类型)仅仅是拷贝了一份引用,因此当skill的值发生改 变时,被克隆对象s的属性skill也将跟随改变
1.定义Javabean类
学生技能类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package com.heima.cloneDemo.domain;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Skill implements Cloneable { private String skillName; @Override protected Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super .clone(); } }
学生类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package com.heima.cloneDemo.domain;@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Student implements Cloneable { private String name; private int age; private Skill skill; @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException { Student stu = (Student) super .clone(); Skill skill = (Skill) this .skill.clone(); stu.setSkill(skill); return stu; } }
2.定义测试类
测试类
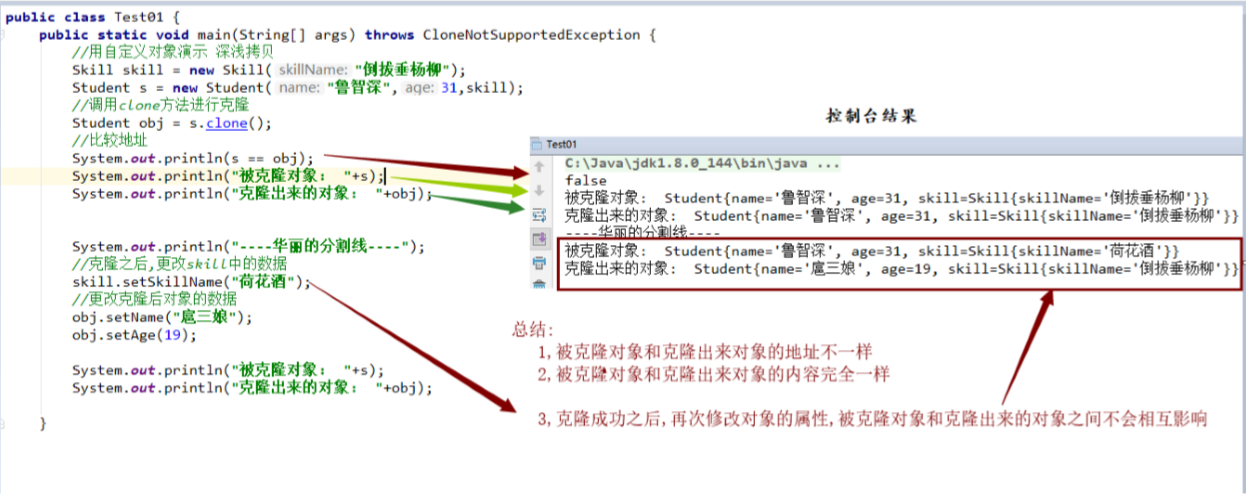
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { Skill skill = new Skill ("倒拔垂杨柳" ); Student s = new Student ("鲁智深" ,31 ,skill); Student obj = s.clone(); System.out.println(s == obj); System.out.println("被克隆对象: " +s); System.out.println("克隆出来的对象: " +obj); System.out.println("----华丽的分割线----" ); skill.setSkillName("荷花酒" ); obj.setName("扈三娘" ); obj.setAge(19 ); System.out.println("被克隆对象: " +s); System.out.println("克隆出来的对象: " +obj); } }
控制台效果
2.3 RandomAccess标记接口
介绍 标记接口由 List 实现使用,以表明它们支持快速(通常为恒定时间)随机访问。 此接口的主要目的是允许通用算法更改其行为,以便在应用于随机访问列表或顺序访问列表时提供良好的性 能。
用于操纵随机访问列表的佳算法(例如 ArrayList )可以在应用于顺序访问列表时产生二次行为(如 LinkedList )。 鼓励通用列表算法在应用如果将其应用于顺序访问列表之前提供较差性能的算法时,检查 给定列表是否为 instanceof ,并在必要时更改其行为以保证可接受的性能。
人们认识到,随机访问和顺序访问之间的区别通常是模糊的。 例如,一些 List 实现提供渐近的线性访问时 间,如果它们在实践中获得巨大但是恒定的访问时间。 这样的一个 List 实现应该通常实现这个接口。 根据 经验, List 实现应实现此接口,如果对于类的典型实例,此循环:
1 2 for (int i=0 , n=list.size(); i < n; i++) list.get(i);
比这个循环运行得更快:
1 2 for (Iterator i=list.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) i.next();
案例演示一·
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { list.add(i+"a" ); } System.out.println("----通过索引(随机访问:)----" ) long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { list.get(i); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("随机访问: " +(endTime-startTime)); System.out.println("----通过迭代器(顺序访问:)----" ); startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ it.next(); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("顺序访问: " +(endTime-startTime)); } }
控制台效果
—-通过索引(随机访问:)—- 随机访问: 2 —-通过迭代器(顺序访问:)—- 顺序访问: 3
案例演示二
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { list.add(i+"a" ); System.out.println("----通过索引(随机访问:)----" ); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { list.get(i); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("随机访问: " +(endTime-startTime)); System.out.println("----通过迭代器(顺序访问:)----" ); startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ it.next(); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("顺序访问: " +(endTime-startTime)); } }
控制台效果
—-通过索引(随机访问:)—- 随机访问: 33759 —-通过迭代器(顺序访问:)—- 顺序访问: 9
为什么LinkedList随机访问比顺序访问要慢这么多? 源码分析 随机访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 list.get(i); public class LinkedList <E> { public E get (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } Node<E> node (int index) { if (index < (size >> 1 )) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) x = x.next; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1 ; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } }
顺序访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public class LinkedList <E>{ public ListIterator<E> listIterator (int index) { checkPositionIndex(index); return new ListItr (index); } private class ListItr implements ListIterator <E> { private Node<E> lastReturned; private Node<E> next; private int nextIndex; private int expectedModCount = modCount; ListItr(int index) { next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); nextIndex = index; } } Node<E> node (int index) { if (index < (size >> 1 )) { for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1 ; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } } private class ListItr implements ListIterator <E> { public boolean hasNext () { return nextIndex < size; } } public class LinkedList <E>{ private class ListItr implements ListIterator <E> { public E next () { checkForComodification(); if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException (); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; return lastReturned.item; } } }
小结 : 由于随机访问的时候源码底层每次都需要进行折半的动作,再经过判断是从头还是从尾部一个个寻找。 而顺序访问只会在获取迭代器的时候进行一次折半的动作,以后每次都是在上一次的基础上获取下一个元素。 因此顺序访问要比随机访问快得
3. ArrayList源码分析 3.1 构造方法
Constructor
Constructor描述
ArrayList()
构造一个初始容量为十的空列表。
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
构造具有指定初始容量的空列表。
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
构造一个包含指定集合的元素的列表,按照它们由集合的迭代器返回 的顺序。
1. 空参构造ArrayList() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); } }
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {} Object[] elementData; public ArrayList () { this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
结论
通过空参构造方法创建集合对象并未构造一个初始容量为十的空列表,仅仅将 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 的地址赋值给elementData
2. 指定容量ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(5 ); } }
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; public ArrayList (int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0 ) { this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); } } }
结论
根据 ArrayList 构造方法参数创建指定长度的数组
3. ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Test03 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("aaa" ); list.add("bbb" ); list.add("ccc" ); ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(list); for (String s : list1) { System.out.println(s); } } }
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; public ArrayList (Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0 ) { if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } } class Arrays { public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); } public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T []> newType) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object [newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); System.arraycopy(original, 0 , copy, 0 , Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; } }
3.2 添加方法
方法名
描述
public boolean add(E e)
将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾。
public void add(int index, E element)
在此列表中的指定位置插入指定的元素。
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
按指定集合的Iterator返回的顺序将指定集合中的所有元素 追加到此列表的末尾。
public boolean addAll(i nt index, Collection<? extends E> c)
将指定集合中的所有元素插入到此列表中,从指定的位置 开始。
添加单个元素 public boolean add(E e) 添加单个元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("黑马程序员" ); } }
源代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } }
在指定索引处添加元素 public void add(int index, E element) 在指定索引处添加元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("黑马程序员" ); list.add("传智播客" ); list.add("传智大学" ); list.add(1 , "长沙校区" ); System.out.println(list); } }
源代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public void add (int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1 , size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void rangeCheckForAdd (int index) { if (index > size || index < 0 ) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } }
将集合的所有元素一次性添加到集合
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 将集合的所有元素一次性添加到集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Test03 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("黑马程序员" ); list.add("传智播客" ); list.add("传智大学" ); ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); list1.addAll(list); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list1); } }
源代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; } }
在指定的索引位置添加集合 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 在指定的索引位置添加集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Test04 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("黑马程序员" ); list.add("传智播客" ); list.add("传智大学" ); ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(); list1.add("酷丁鱼" ); list1.add("博学谷" ); list1.addAll(1 ,list); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list1); } }
源代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean addAll (int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; } private void rangeCheckForAdd (int index) { if (index > size || index < 0 ) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } } public final class System { 参数 src - 源数组。 srcPos - 源数组中的起始位置。 dest - 目标数组。 destPos - 目的地数据中的起始位置。 length - 要复制的数组元素的数量。 public static void arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest,int destPos,int length) }
3.3 删除方法 根据索引删除元素 public E remove(int index) 根据索引删除元素
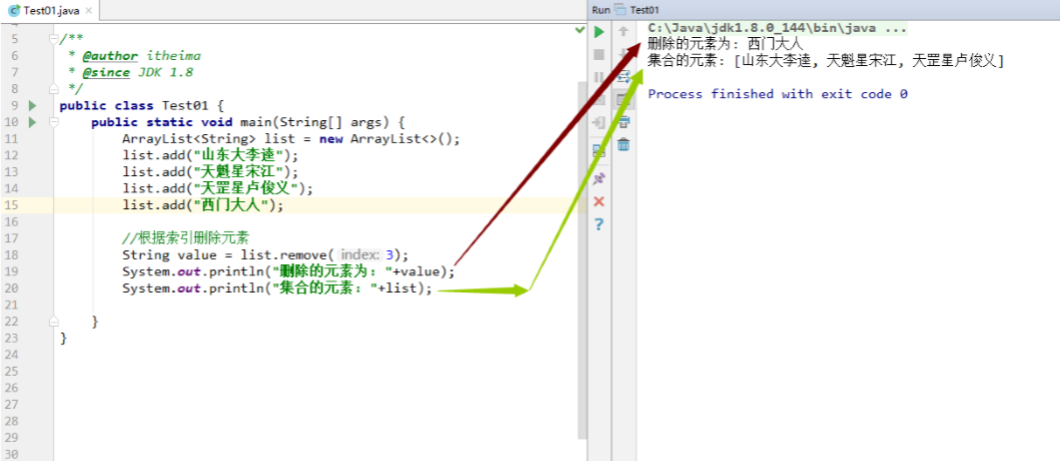
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("山东大李逵" ); list.add("天魁星宋江" ); list.add("天罡星卢俊义" ); list.add("西门大人" ); String value = list.remove(3 ); System.out.println("删除的元素为: " +value); System.out.println("集合的元素: " +list); } }
效果图
源代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class ArrayList <E> { public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index,numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; return oldValue; } }
根据元素删除元素 public boolean remove(Object o) 根据元素删除元素
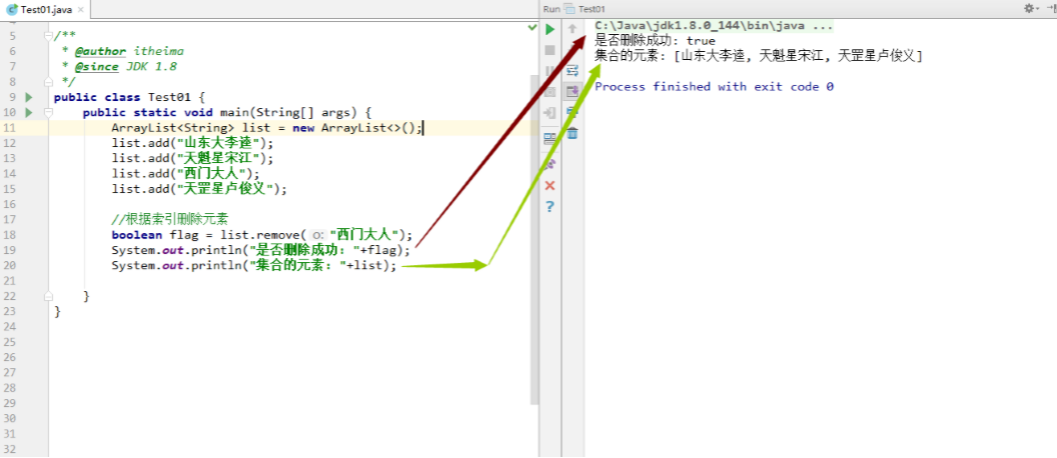
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("山东大李逵" ); list.add("天魁星宋江" ); list.add("西门大人" ); list.add("天罡星卢俊义" ); boolean flag = list.remove("西门大人" ); System.out.println("是否删除成功: " +flag); System.out.println("集合的元素: " +list); } }
效果
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class ArrayList <E> { public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index,numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; } }
3.4 修改方法 根据索引修改集合元素 public E set(int index, E element) 根据索引修改集合元素
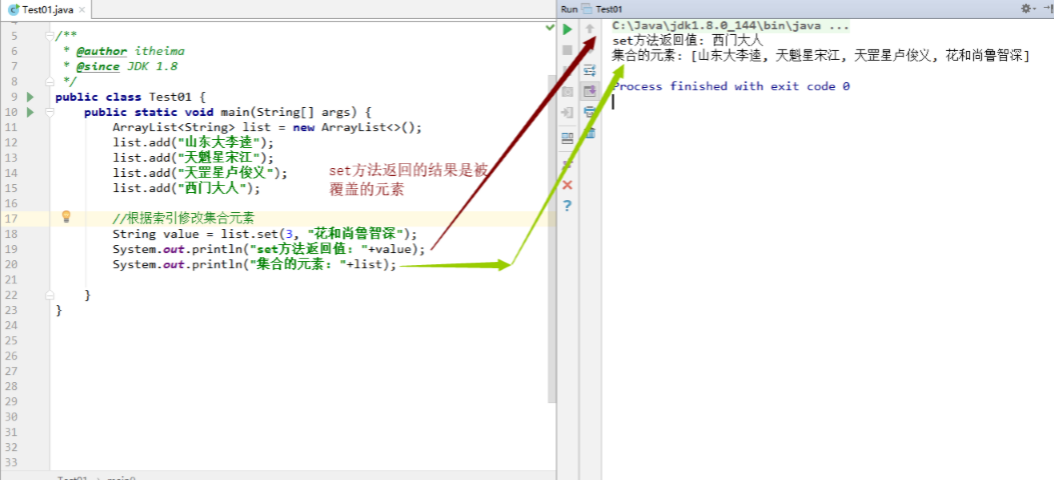
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("山东大李逵" ); list.add("天魁星宋江" ); list.add("天罡星卢俊义" ); list.add("西门大人" ); String value = list.set(3 , "花和尚鲁智深" ); System.out.println("set方法返回值: " +value); System.out.println("集合的元素: " +list); } }
效果
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public E set (int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } private void rangeCheck (int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } }
3.5 获取方法 根据索引获取元素 public E get(int index) 根据索引获取元素
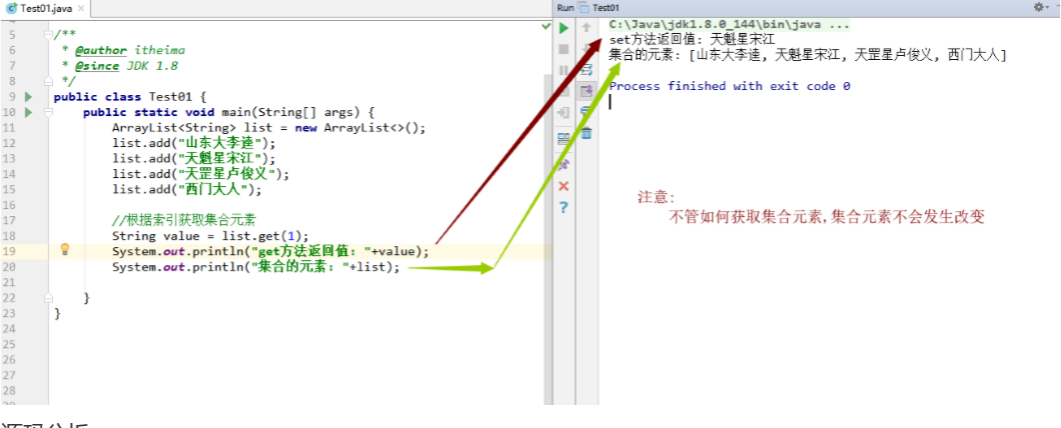
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("山东大李逵" ); list.add("天魁星宋江" ); list.add("天罡星卢俊义" ); list.add("西门大人" ); String value = list.get(1 ); System.out.println("get方法返回值: " +value); System.out.println("集合的元素: " +list); } }
效果
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public E get (int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } private void rangeCheck (int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } }
3.6 转换方法 把集合所有数据转换成字符串 public String toString() 把集合所有数据转换成字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("山东大李逵" ); list.add("天魁星宋江" ); list.add("天罡星卢俊义" ); list.add("西门大人" ); String str = list.toString(); System.out.println(str); } }
效果
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; } public abstract class AbstractCollection <E> { public String toString () { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (! it.hasNext()) return "[]" ; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append('[' ); for (;;) { E e = it.next(); sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); if (! it.hasNext()) return sb.append(']' ).toString(); sb.append(',' ).append(' ' ); } } }
3.7 迭代器 普通迭代器 public Iterator iterator() 普通迭代器
案例一 : 已知集合:List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素:”hello”、”Java”、”PHP”,使用迭代器遍 历获取集合的每一个元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("Java" ); list.add("PHP" ); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String s = it.next(); System.out.println(s); } } }
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public Iterator<E> iterator () { return new Itr (); } private class Itr implements Iterator <E> { int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext () { return cursor != size; } public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } }
案例二 : 已知集合:List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素:”hello”、”Java”、”PHP”,使用迭代器遍 历集合看有没有”PHP”这个元素,如果有,就使用集合对象删除该元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("Java" ); list.add("PHP" ); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String s = it.next(); if (s.equals("PHP" )) { list.remove("PHP" ); } } } }
控制台结果:并发修改异常
Exception in thread “main” java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at
java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:901) at
java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:851) at cn.itheima.method.Test01.main(Test01.java:24)
源码分析 :(应该从获取迭代器的时候就进入到源代码中 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } public Iterator<E> iterator () { return new Itr (); } private class Itr implements Iterator <E> { int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext () { return cursor != size; } public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; } } 结论: 一,集合每次调用add方法的时候,实际修改次数变量的值都会自增一次 二,在获取迭代器的时候,集合只会执行一次将实际修改集合的次数赋值给预期修改集合的次数 三,集合在删除元素的时候也会针对实际修改次数的变量进行自增的操作
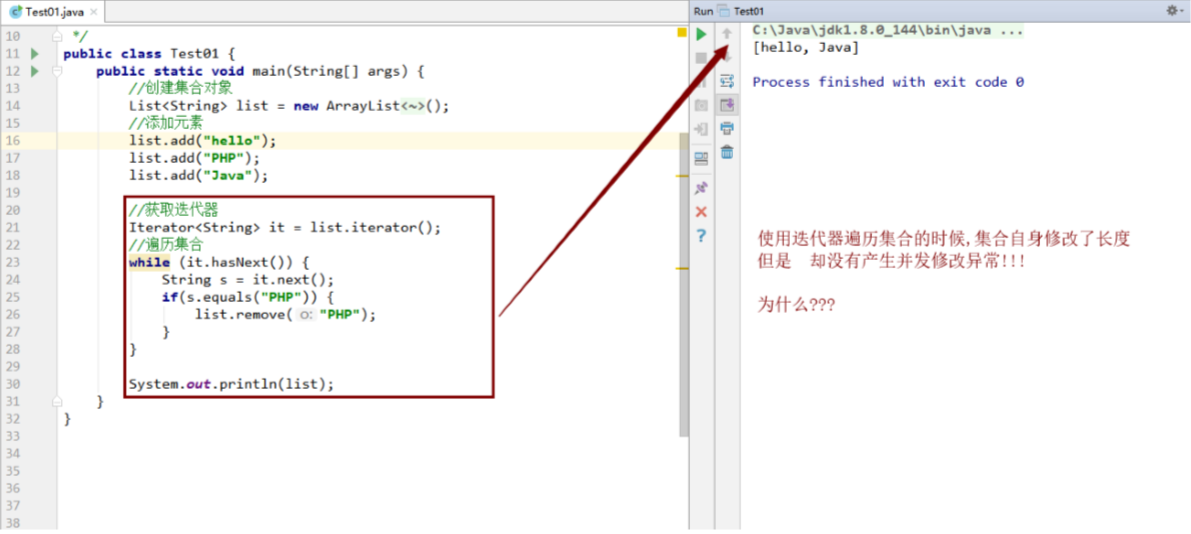
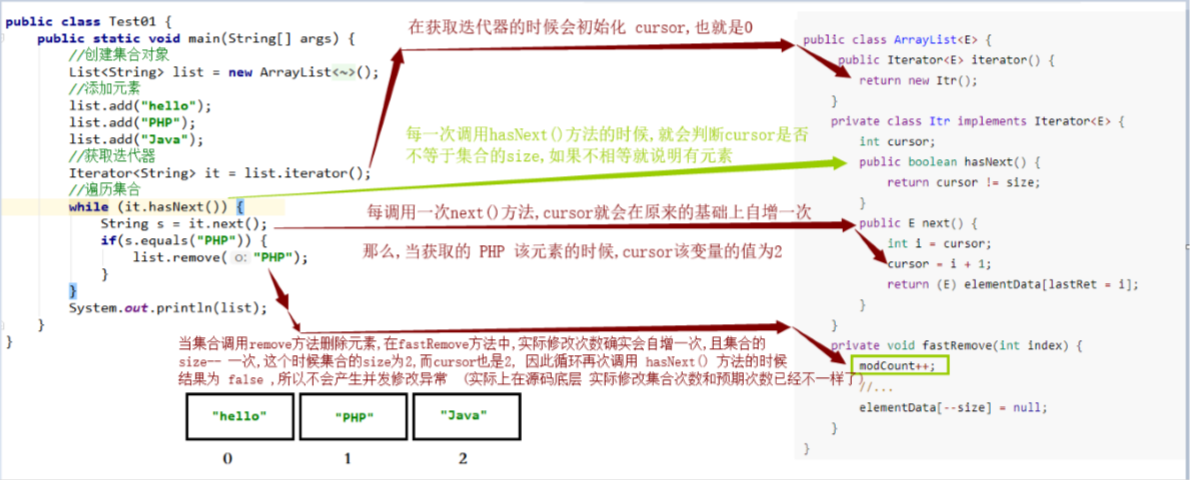
案例三 :已知集合:List list = new ArrayList();里面有三个元素:”hello”、”PHP”、”JavaSE”,使用迭代器 遍历集合看有没有”PHP”这个元素,如果有,就使用集合对象删除该元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Test03 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String s = it.next(); if (s.equals("PHP" )) { list.remove("PHP" ); } } System.out.println(list); } }
结果图
结论
1 2 3 4 5 结论: 当要删除的元素在集合的倒数第二个位置的时候,不会产生并发修改异常 原因: 是因为在调用hasNext方法的时候,光标的值和集合的长度一样,那么就会返回false 因此就不会再去调用next方法获取集合的元素,既然不会调用next方法那么底层就不会产生并发修改异常
图解
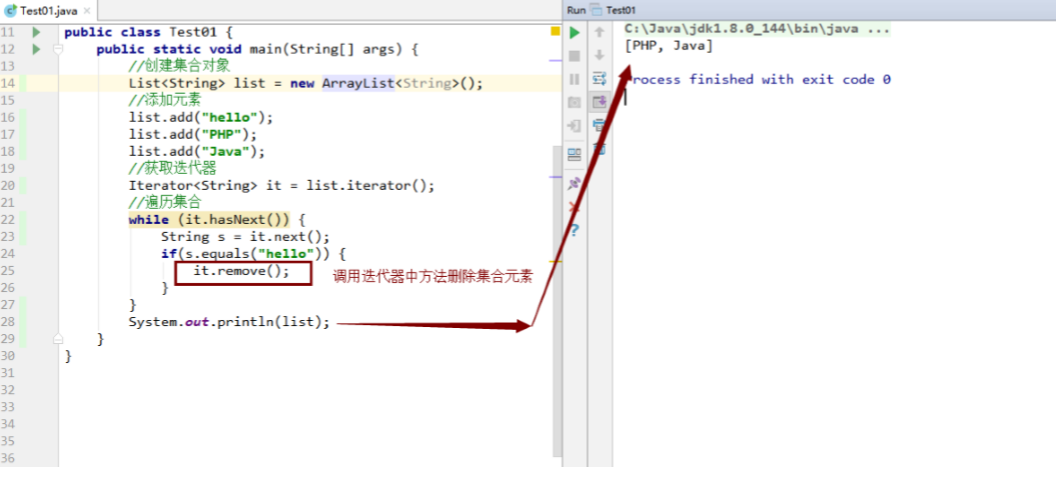
迭代器中的remove方法(不是上面Arraylist中的),删除集合中的元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class Test04 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String s = it.next(); if (s.equals("hello" )) { it.remove(); } } System.out.println(list); } }
结果图
源码分析(应该从获取迭代器的时候就进入到源代码中)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } public Iterator<E> iterator () { return new Itr (); } private class Itr implements Iterator <E> { int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext () { return cursor != size; } public void remove () { if (lastRet < 0 ) throw new IllegalStateException (); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this .remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1 ; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; } public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; return oldValue; } } 结论: 一,迭代器调用remove方法删除元素,其实底层真正还是调用集合自己的删除方法来删除元素 二,在调用remove方法中会每次都给预期修改次数的变量赋值
3.8 清空方法 清空集合所有数据 public void clear() 清空集合所有数据
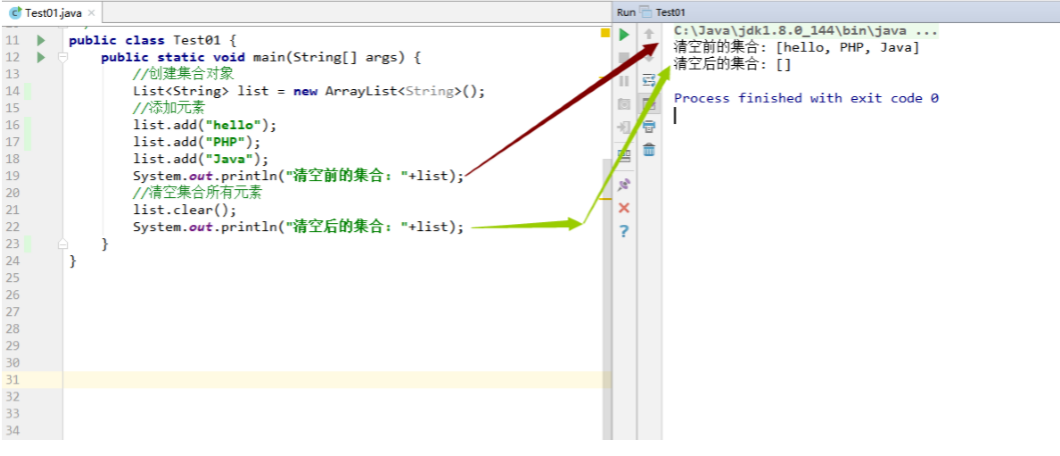
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); System.out.println("清空前的集合: " +list); list.clear(); System.out.println("清空后的集合: " +list); } }
效果图
源码分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public void clear () { modCount++; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null ; size = 0 ; } }
3.9 包含方法 判断集合是否包含指定元素 public boolean contains(Object o) 判断集合是否包含指定元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); if (!list.contains("JavaSE" )){ list.add("JavaSE" ); } System.out.println(list); } private static void method (List<String> list) { boolean flag = false ; for (String value : list) { if (value.equals("JavaSE" )){ flag = true ; break ; } } if (!flag){ list.add("JavaSE" ); } System.out.println(list); } }
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean contains (Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0 ; } public int indexOf (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null ) return i; } else { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1 ; } }
3.10 判断集合是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); boolean b = list.isEmpty(); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(list); } }
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class ArrayList <E> { private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; Object[] elementData; private int size; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public boolean isEmpty () { return size == 0 ; } }
4. 面试题 4.1 ArrayList是如何扩容的? 源码分析过程中已经讲解
第一次扩容10
以后每次都是原容量的1.5倍
4.2 ArrayList频繁扩容导致添加性能急剧下降,如何处理? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Test01 { public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <String>(); list.add("hello" ); list.add("PHP" ); list.add("Java" ); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { list.add(i+"" ); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("添加10W条数据用时: " + (endTime - startTime)); System.out.println("-----------------------------" ); List<String> list1 = new ArrayList <>(10000 ); startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) { list1.add(i+"" ); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("添加10W条数据用时: " + (endTime - startTime)); } } 添加10W条数据用时: 39 ----------------------------- 添加10W条数据用时: 4
4.3 ArrayList插入或删除元素一定比LinkedList慢么? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class Test02 { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList <String>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5000000 ; i++) { arrayList.add(i+"黑马" ); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); String value = arrayList.remove(50000 ); System.out.println(value); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("ArrayList集合删除元素的时间: " +(endTime-startTime)); LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList <String>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5000000 ; i++) { linkedList.add(i+"黑马" ); } startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); value = arrayList.remove(50000 ); System.out.println(value); endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("LinkedList集合删除元素的时间: " +(endTime-startTime)); } } 50000 黑马ArrayList集合删除元素的时间: 5 50001 黑马LinkedList集合删除元素的时间: 4
4.4 ArrayList是线程安全的么? 4.5 如何复制某个ArrayList到另一个ArrayList中去?
使用clone()方法
使用ArrayList构造方法
使用addAll方法
以上三种方式都在前面有讲
4.6 已知成员变量集合存储N多用户名称,在多线程的环境下,使用迭代器在读 取集合数据的同时如何保证还可以正常的写入数据到集合? 4.7 ArrayList 和 LinkList区别?
5. 自定义ArrayList 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 package com.zzxx.customArrayList;public class MyArrayList <E> { private Object[] elementData; private int size; private Object[] emptyArray = {}; private final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; public MyArrayList () { elementData = emptyArray; } public boolean add (E e) { grow(); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } private void grow () { if (elementData == emptyArray){ elementData = new Object [DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; } if (size == elementData.length){ int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); Object[] obj = new Object [newCapacity]; System.arraycopy(elementData, 0 , obj, 0 , elementData.length); elementData = obj; } } public String toString () { if (size == 0 ){ return "[]" ; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append("[" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { if (i == size-1 ){ sb.append(elementData[i]).append("]" ); }else { sb.append(elementData[i]).append("," ).append(" " ); } } return sb.toString(); } public E set (int index, E element) { checkIndex(index); E value = (E) elementData[index]; elementData[index] = element; return value; } private void checkIndex (int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("索引越界了!" ); } } public E remove (int index) { checkIndex(index); E value = (E) elementData[index]; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ){ System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); } elementData[--size] = null ; return value; } public E get (int index) { checkIndex(index); return (E) elementData[index]; } public int getSize () { return size; } }