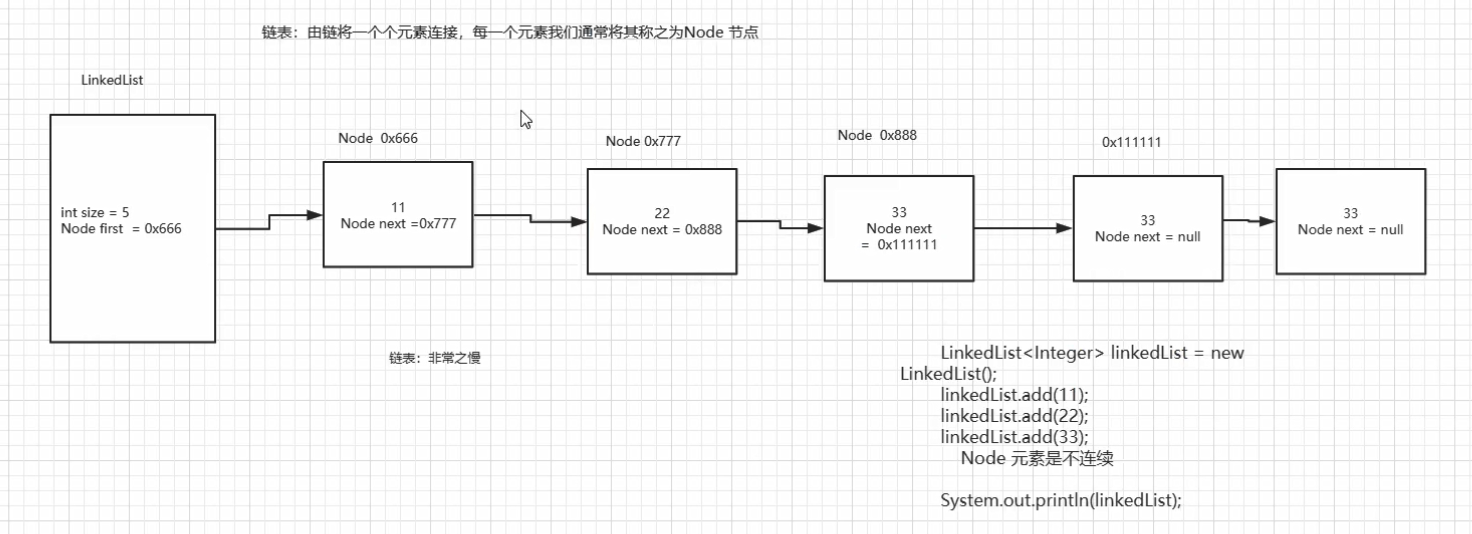
链表 目的
链表的介绍
手写单链表&双链表
LinkedList 源码阅读
LinkedList 并发修改异常
LinkedList 多线程安全问题的产生和解决
一、ArrayList引发的思考
优点:查询快
缺点
1、增删慢,消耗cpu的性能
情况一、指定索引上的添加
情况二、如果原数组中的元素已经不够了
2、比较浪费内存空间
有没有一种数据结构可以用多少个空间就申请多少个空间,并且又能够提高他的增删速度呢?
二、链表 链表的分类:单链表,双链表,循环链表
三、自定义单向链表 设计接口
目的:为了体系的完整,以及代码的复用,设计出以下结构
需要实现的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public int size () ;public boolean isEmpty () ;public boolean contains (E element) ;public void add (E element) ;public E get (int index) ;public E set (int index,E element) ;public void add (int index, E element) ;public E remove (int index) ;public int indexOf (E element) ;public void clear () ;public String toStrin () ;
3.1 List 接口 包含共性的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public interface List <E>{ int size () boolean isEmpty () boolean contains (E element) void add (E element) E get (int index) E set (int index,E element) void add (int index, E element) E remove (int index) int indexOf (E element) void clear () }
3.2 AbstractList 抽象类 实现共性的方法,实现List
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public abstract class AbstractList implements List <E>{ int size; int size () { } boolean isEmpty () { } boolean contains (E element) { } void add (E element) { } } public class LinkedList <E> extends AbstractList <E> { }
将ArrayList 和 LinkedList 都 继承AbstractList
3.3 实现 AbstractList 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public abstract class AbstractList <E> implements List <E>{ protected int size = 0 ; @Override public int size () { return size; } @Override public boolean isEmpty () { return size == 0 ; } @Override public boolean contains (E element) { return indexOf(element) != -1 ; } @Override public void add (E element) { add(size,element); } }
LinkedList 实现(单向链表) 顺序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 import com.zzxx.dynamic.abstractclass.AbstractList;public class LinkedList <E> extends AbstractList <E> { private Node first; private static class Node <E> { Node<E> next; E element; public Node (Node next, E element) { this .next = next; this .element = element; } } @Override public E get (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node( ).element; } private void checkElementIndex (int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (": Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size); } } private boolean isElementIndex (int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; } private Node<E> node (int index) { Node x = first; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) { x = x.next; } return x; } @Override public E set (int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> node = node(index); E oldElement = node.element; node.element = element; return oldElement; } @Override public void add (int index, E element) { checkPostionIndex(index); if (index == 0 ){ first = new Node (first,element); }else { Node<E> pre = node(index - 1 ); Node<E> next = pre.next; pre.next = new Node <E>(next,element); } size++; } private void checkPostionIndex (int index) { if (!isPostionIndex(index)){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (": Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size); } } private boolean isPostionIndex (int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } @Override public E remove (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> oldNode = first; if (index == 0 ){ first = first.next; }else { Node<E> pre = node(index - 1 ); oldNode = pre.next; pre.next = oldNode.next; } return oldNode.element; } @Override public int indexOf (E element) { Node x = first; int index = 0 ; if (element == null ) { for (Node i = x; i != null ; i = i.next) { if (element == i.element){ return index; } index ++; } } else { for (Node i = x; i != null ; i = i.next) { if ( element.equals(i.element)){ return index; } index ++; } } return -1 ; } @Override public void clear () { size = 0 ; first = null ; } public String toString () { if (size == 0 ){ return "[]" ; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ().append("[" ); Node x = first; for (Node i = x; i != null ; i = i.next){ sb.append(i.element); if ( i.next == null ){ return sb.append("]" ).toString(); } sb.append("," ); } return sb.toString(); } }
四、将单链表改造成双向链表 4.1 双向链表 可以从前指向后,也可以从后去指向前
LinkedList 内部 size first last
以及Node
E element
Node next
Node pre
双向链表遍历效率可能优于单向链表
原因:双向链表可以在查找元素时,判断靠近头还是靠近尾,如果靠近头从头开始找,如果靠近尾从尾开始找
4.2 双向链表的实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public void add (int index, E element) {checkPostionIndex(index); if (index == size){ linkLast(element); }else { linkBefore(element,node(index)); } size++; private void linkLast (E element) { Node l = last; Node newNode = new Node (l,null ,element); last = newNode; if ( l == null ){ first = newNode; }else { l.next = newNode; } } private void linkBefore (E element,Node node) { Node<E> pre = node.pre; Node<E> newNode = new Node (pre,node,element); node.pre = newNode; if (pre == null ){ first = newNode; }else { pre.next =newNode; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public E remove (int index) {checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> node = node(index); Node<E> pre = node.pre; Node<E> next = node.next; if (pre == null ){ first = next; next.pre = null ; }else { pre.next = next; } if (next == null ){ last = pre; }else { next.pre = pre; } size -- ; return node.element;}
1 2 3 4 5 public void clear () { size = 0 ; first = null ; last = null ; }
五、LinkedList 源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 private class ListItr implements ListIterator <E> { private Node<E> lastReturned; private Node<E> next; private int nextIndex; private int expectedModCount = modCount; ListItr(int index) { next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); nextIndex = index; } public boolean hasNext () return nextIndex < size; } public E next () { checkForComodification(); if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException (); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; return lastReturned.item; } public boolean hasPrevious () { return nextIndex > 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class TestLinkedList { public static void main (String[] args) { LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList (); linkedList.add(1 ); linkedList.add(2 ); linkedList.add(3 ); ListIterator iterator = linkedList.listIterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ iterator.add(10 ); System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } }
六、 多线程LinkedList 不安全情况 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class LInkedListThread { public static void main(String[] args) { /* LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList(); Collection ts = Collections.synchronizedCollection(linkedList);*/ ConcurrentLinkedQueue concurrentLinkedQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); // cas 无锁化机制 volatile 关键字来解决的 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { concurrentLinkedQueue.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,10)); System.out.println(concurrentLinkedQueue); } }).start(); } } }