课程导学 会Ant,会Maven,为什么还要学会Gradle
一款最新的 ,功能最强大的构建 工具,用它逼格更高
使用程序代替传统的XML配置,项目构建更灵活
丰富的第三方插件,让你随心所欲使用
完善Android,Java开发技术体系
提升自动化构建技术深度
进阶为高级工程师
1. Gradle相关介绍及开发环境搭建 领域特定语言DSL介绍
全称domain specific language
有哪些常见的DSL语言及特点.
SQL,CSS,HTML,Shell,JSON等等
DSL语言有别于其他通用语言如:C++,Java,C#,DSL常在特殊的场景或领域中使用
通用语言大而全,DSL语言小而细
◆核心思想: 求专不求全 解决特定问题
groovy介绍
是一种基于JVM的敏捷开发语言
结合 了Python、Ruby和Smalltalk的许 多强大的特性
groovy可以 与Java完美结合,而且可以使用java所有的库
groovy特性
语法上支持动态类型,闭包等新一代语言特性
无缝集成所有已经存在的Java类库
即支持面向对 象编程也支持面向过程编程
groovy优势
一种更加敏捷的编程语言
入门非常的容易, 但功能非常的强大
即可以作为编程语宫也可以作为脚本语言
熟练掌握Java的同学会非常容易掌握Groovy
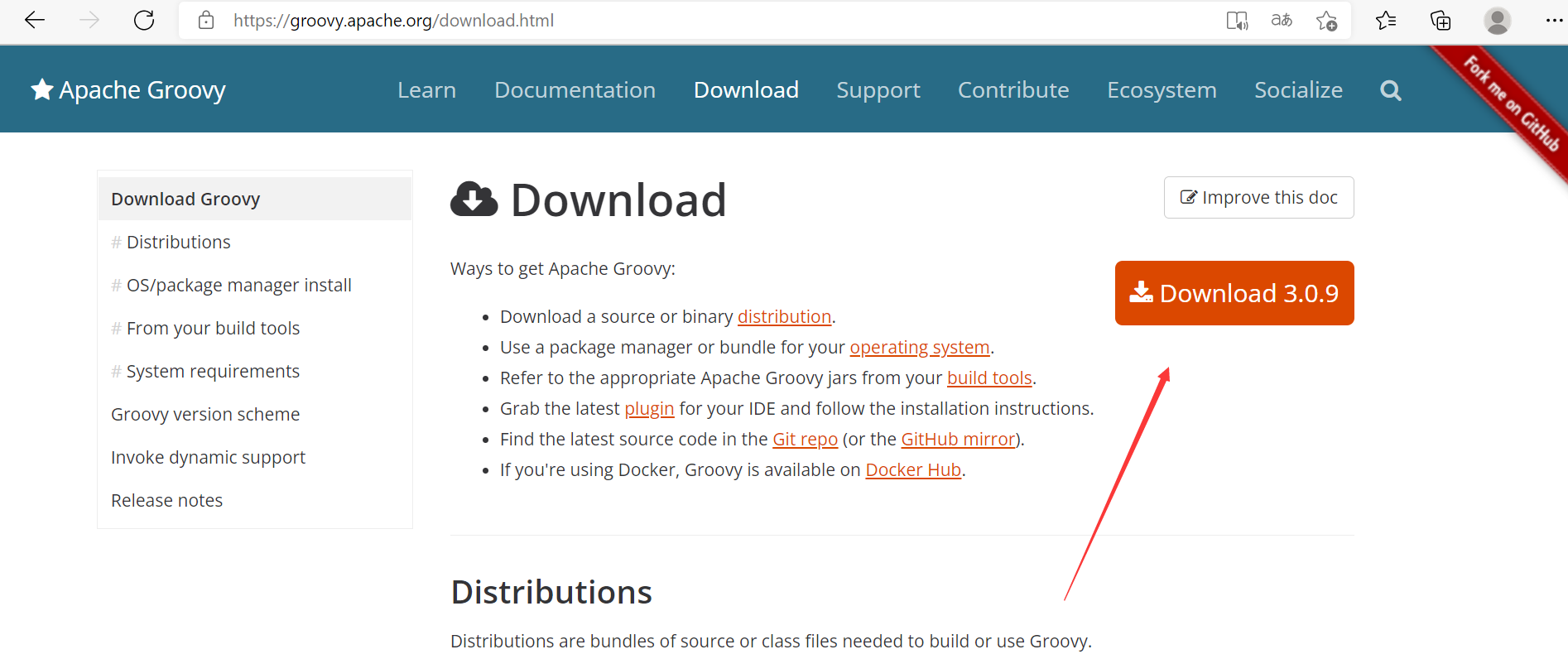
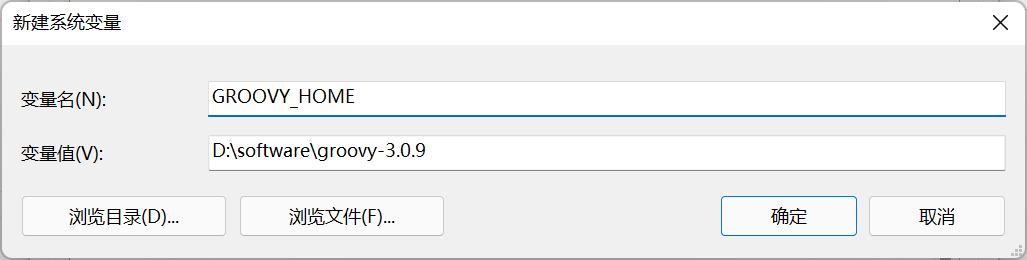
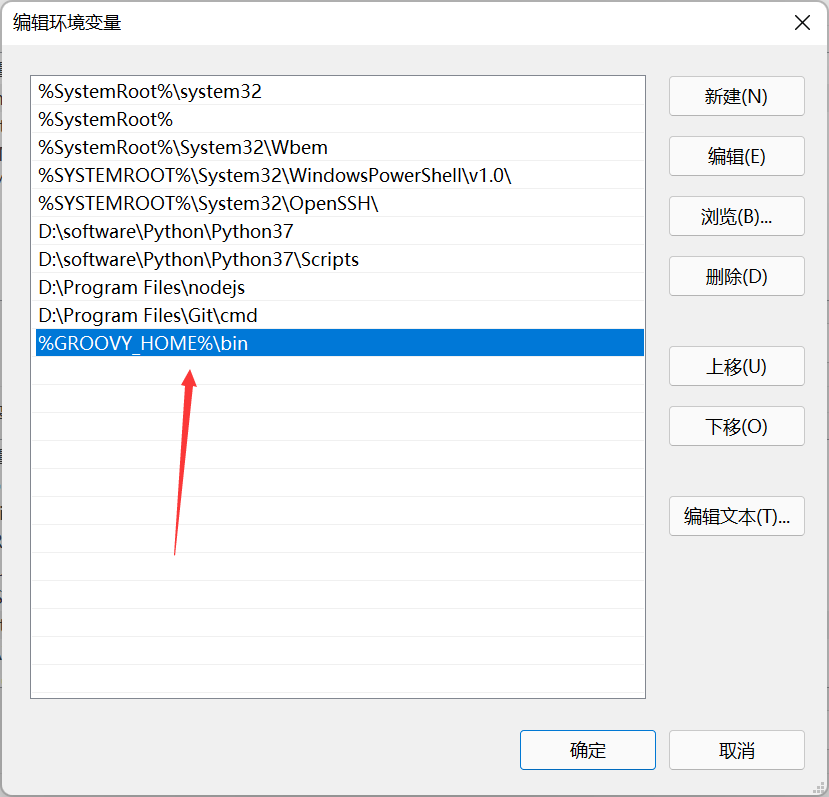
Linux下环境的搭建
安装好JDK环境
到官网下载groovySDK ,解压到合适的位置
添加到环境变量
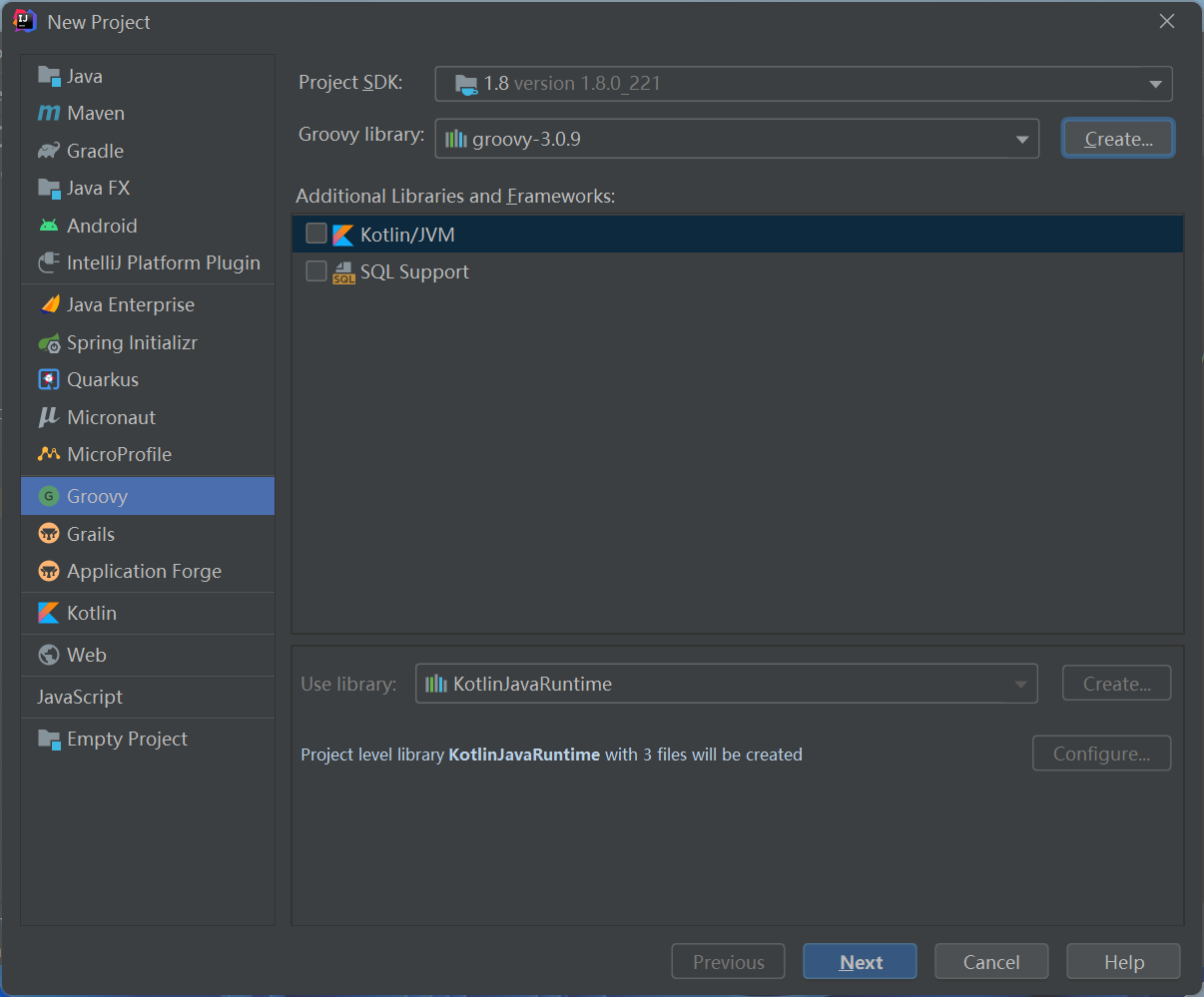
创建groovy工程
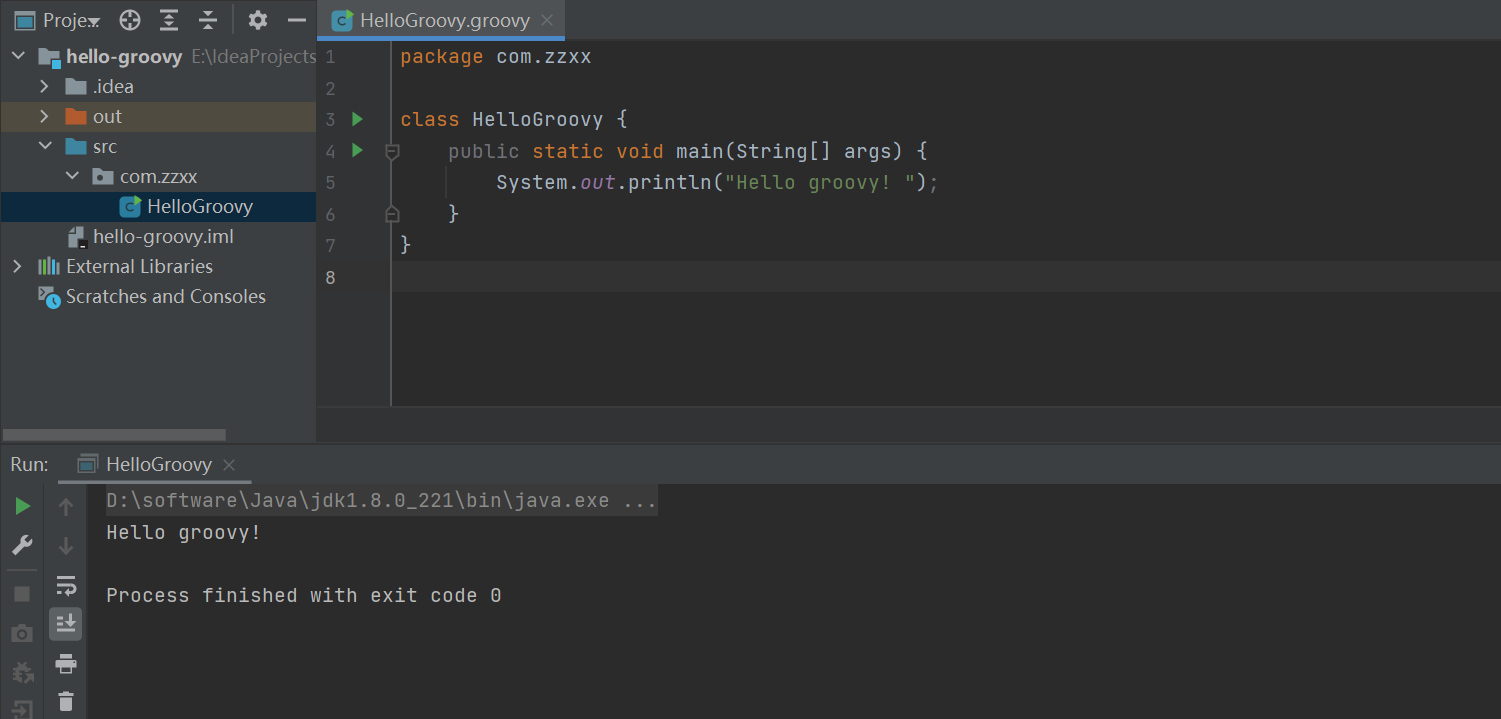
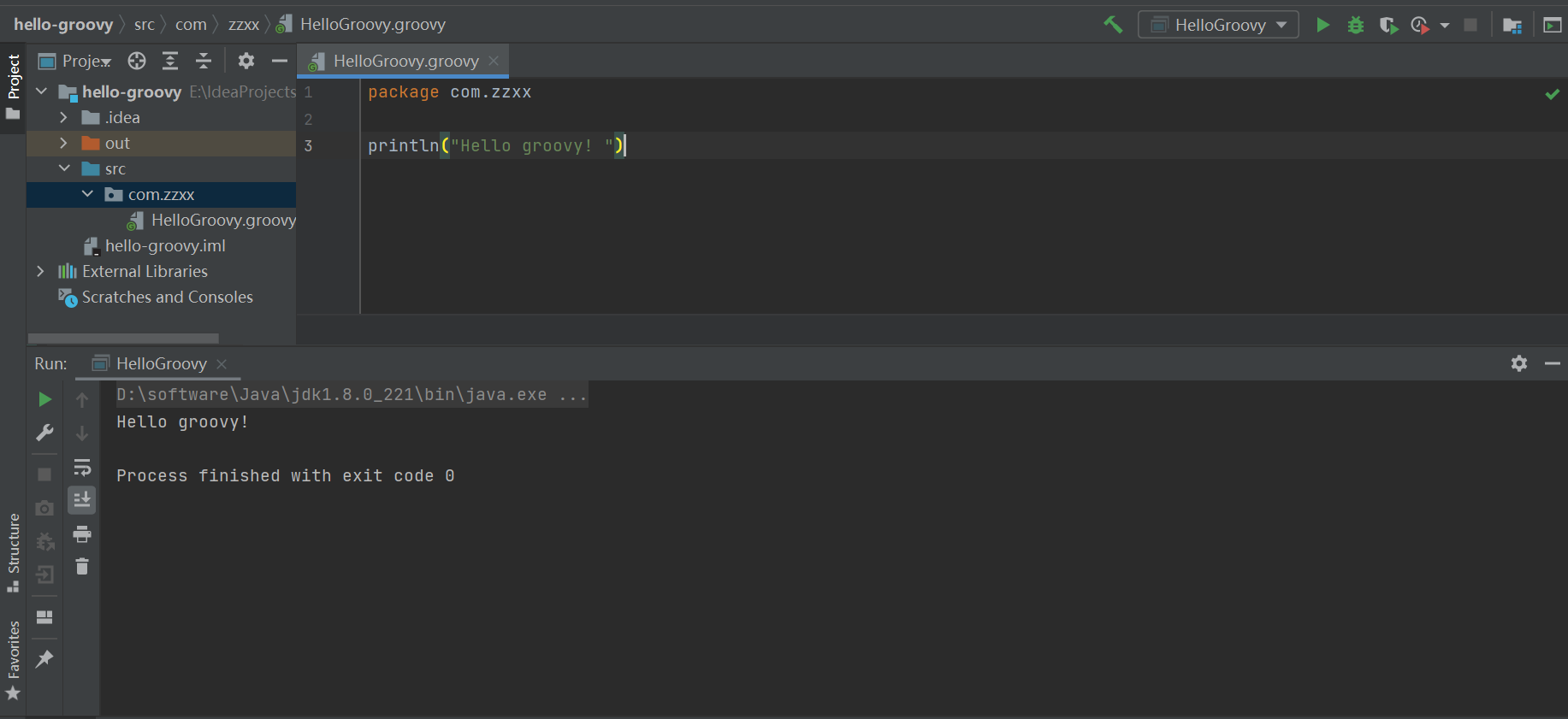
永远的HelloWrold
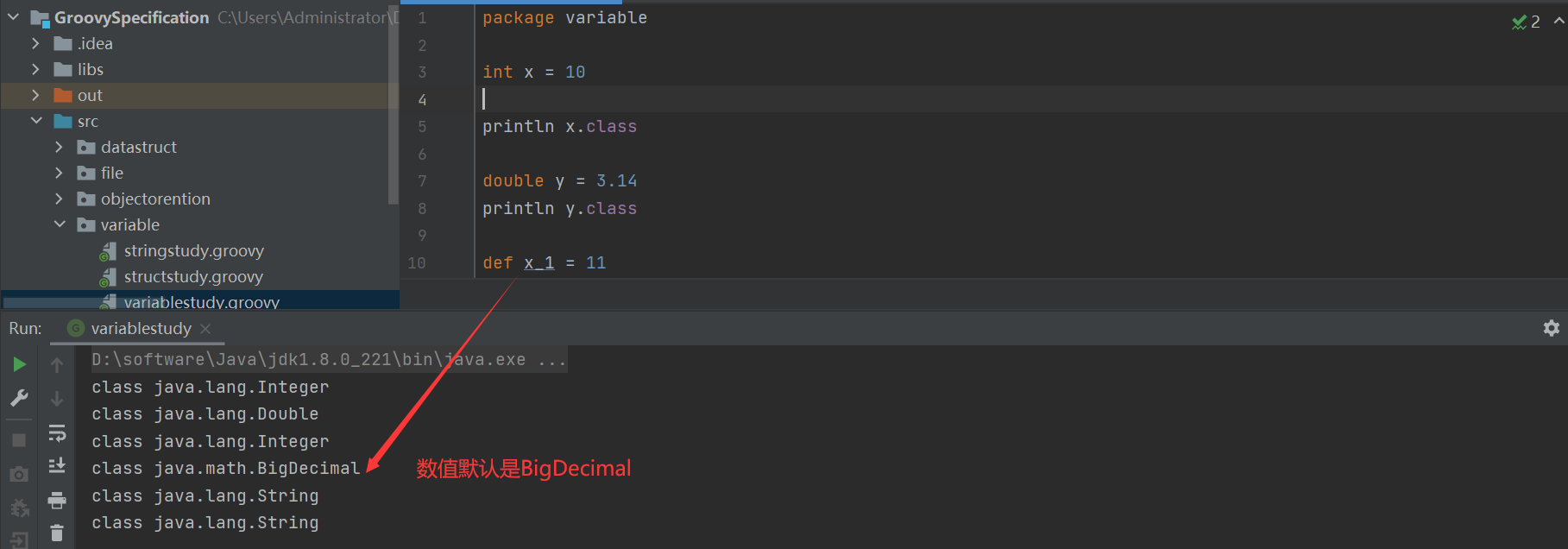
2. Gradle核心语法讲解及实战 groovy基础语法 groovy中的变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package variableint x = 10 println x.class double y = 3.14 println y.class def x_1 = 11 println x_1.class def y_1 = 3.1415 println y_1.class def name = 'Qndroid' println name.class x_1 = 'Test' println x_1.class
groovy中字符串 字符串
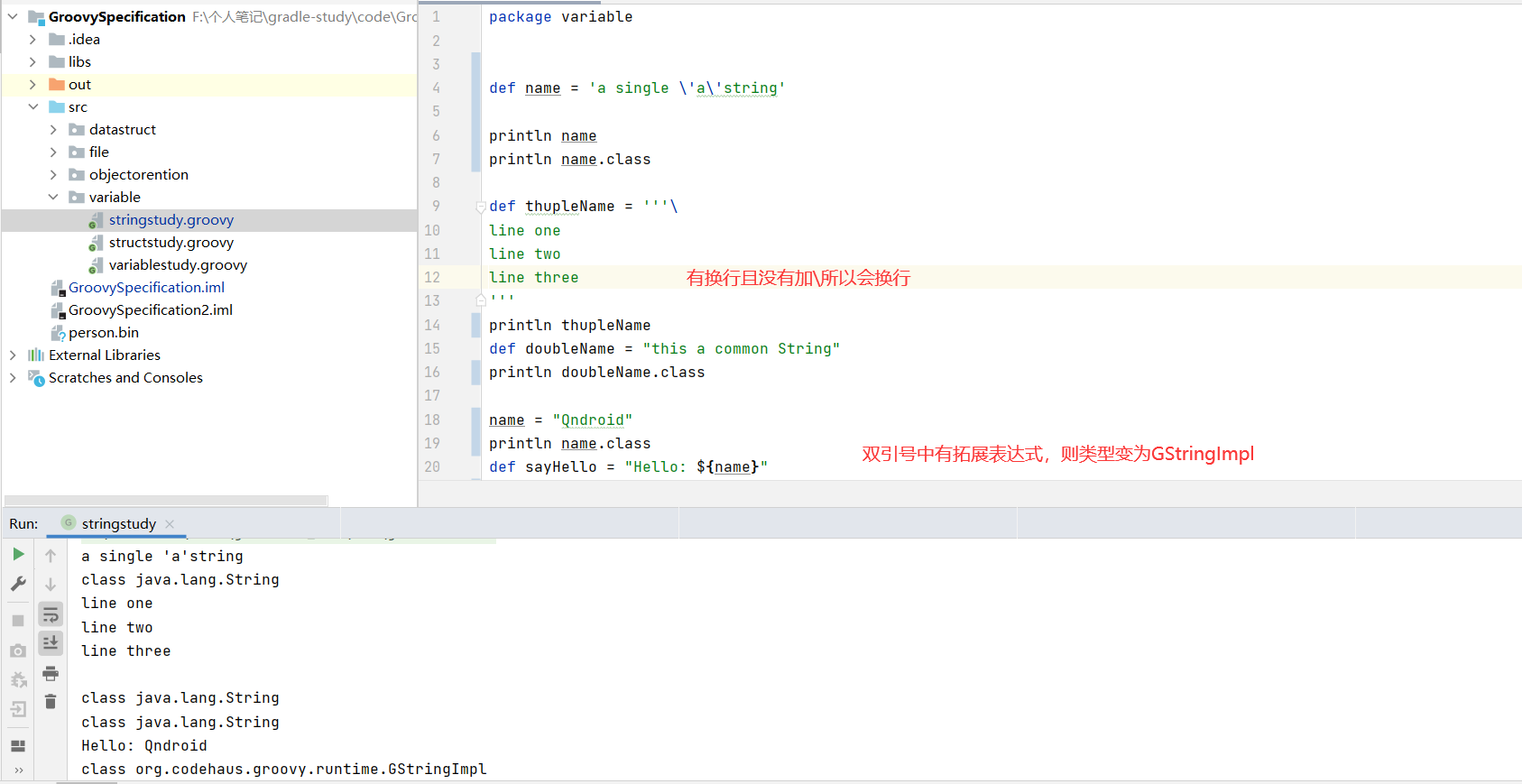
默认 单引号、双引号、还是三引号创建的都为 java.lang.String 类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package variabledef name = 'a single \'a\'string' println name println name.class def thupleName = '''\ line one line two line three ''' println thupleName def doubleName = "this a common String" println doubleName.class name = "Qndroid" println name.class def sayHello = "Hello: ${name}" println sayHello Hello: Qndroid println sayHello.class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def sum = "the sum of 2 and 3 equals ${2 + 3}" println sum def result = echo(sum) println result.class String echo(String message) { return message }
字符串方法详解 String方法
java.lang.String
DefaultGroovyMethods
stringGroovyMethods
字符串填充
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def str = "groovy" println str.center(9 ,"c" ) println str.padLeft(9 , 'a' ) println str.padRight(9 , 'b' )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def str = "groovy Hello" def str2 = 'Hello' println str > str2 println str[0 ] println str[0. .4 ] println str - str2 println str.minus(str2)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def str = "groovy Hello" println str.reverse() println str.capitalize() println str.isNumber()
逻辑控制
顺序逻辑
条件逻辑
循环逻辑
switch/case
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package variabledef x = 1.23 def resultswitch (x) { case 'foo' : result = 'found foo' break case 'bar' : result = 'bar' break case [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 'inlist' ]: result = 'list' break case 12. .30 : result = 'range' break case Integer: result = 'integer' break case BigDecimal: result = 'big decimal' break default: result = 'default' }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 def sum = 0 for (i in 0. .9 ) { sum += i } sum = 0 for (i in [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]) { sum += i } for (i in ['lili' : 1 , 'luck' : 2 , 'xiaoming' : 3 ]) { sum += i.value }
groovy闭包讲解 groovy中闭包基础详解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package variabledef clouser= {println ("Hello Groovy" )} clouser.call() clouser()
1 2 3 4 def clouser= { String name -> println("Hello ${name}" )}def name = "zzxx" clouser(name)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package variabledef clouser= { String name , int age -> println("Hello ${name} my age is $age" ) } def name = "zzxx" clouser(name,12 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package variabledef clouser= { println("Hello ${it} " ) } def name = "zzxx" clouser(name)
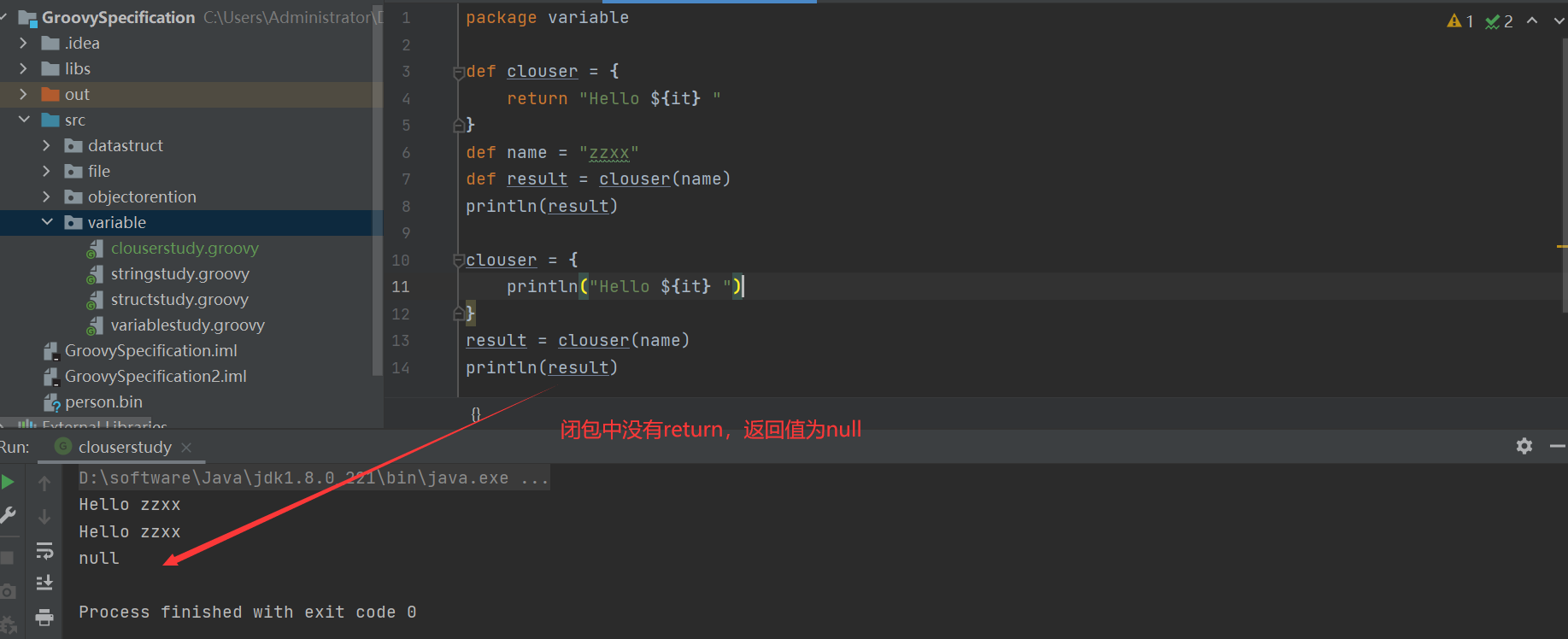
groovy 中闭包一定有返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package variabledef clouser = { return "Hello ${it} " } def name = "zzxx" def result = clouser(name)println(result) clouser = { println("Hello ${it} " ) } result = clouser(name) println(result)
groovy中闭包使用详解 与基本类型的结合使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package variableint fab(int number) { int result = 1 1. upto(number, { num -> result *= num }) return result } int fab2(int number) { int result = 1 number.downto(1 ) { num -> result *= num } return result } println fab(5 ) println fab2(5 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int cal(int number) { int result = 0 number.times { num -> result += num } return result } println cal(101 )
与String结合使用
1 2 3 4 def str = "Hello Groovy" str.each { String temp -> print temp.multiply(2 ) } println str.each { String temp -> temp }
1 println str.find{String s -> s.isNumber()}
1 2 def list = str.findAll({ s -> s.isNumber()})println list.toListString()
1 println str.any {s -> s.isNumber()}
1 println str.every {s -> s.isNumber()}
1 2 list = str.collect {s->s.toUpperCase()} printl list
groovy中闭包进阶讲解
这方面最能体现groovy中闭包比JS的闭包,Java的lambda强大的地方
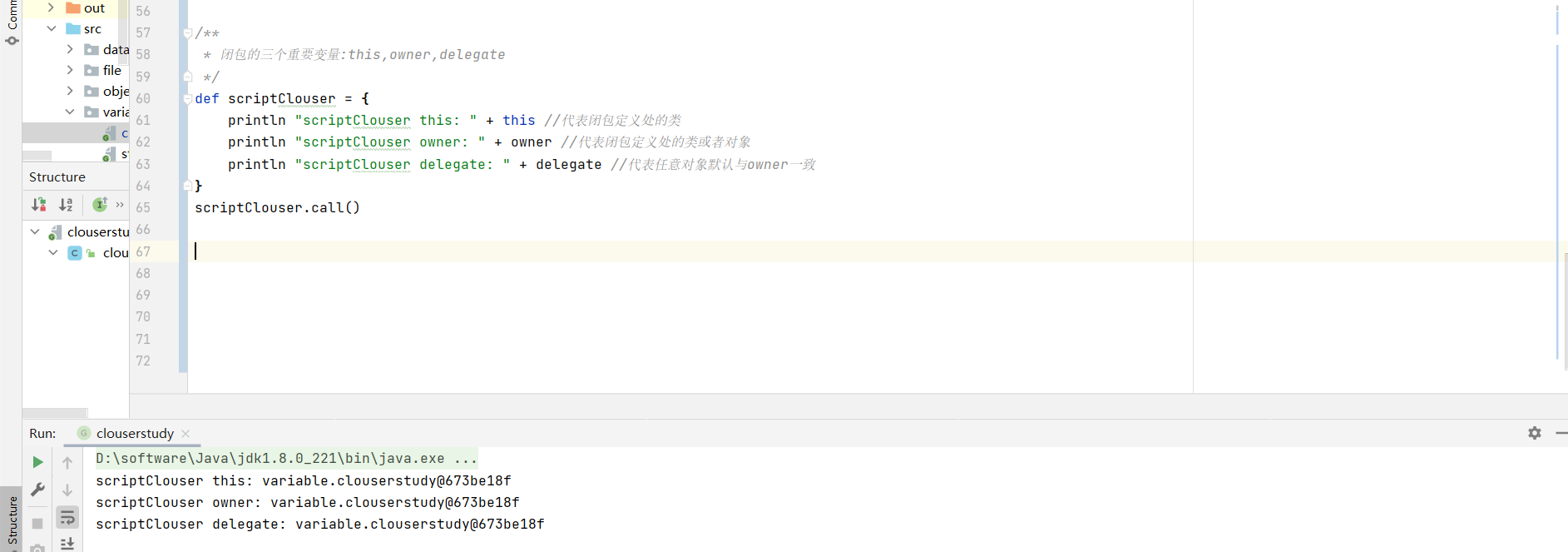
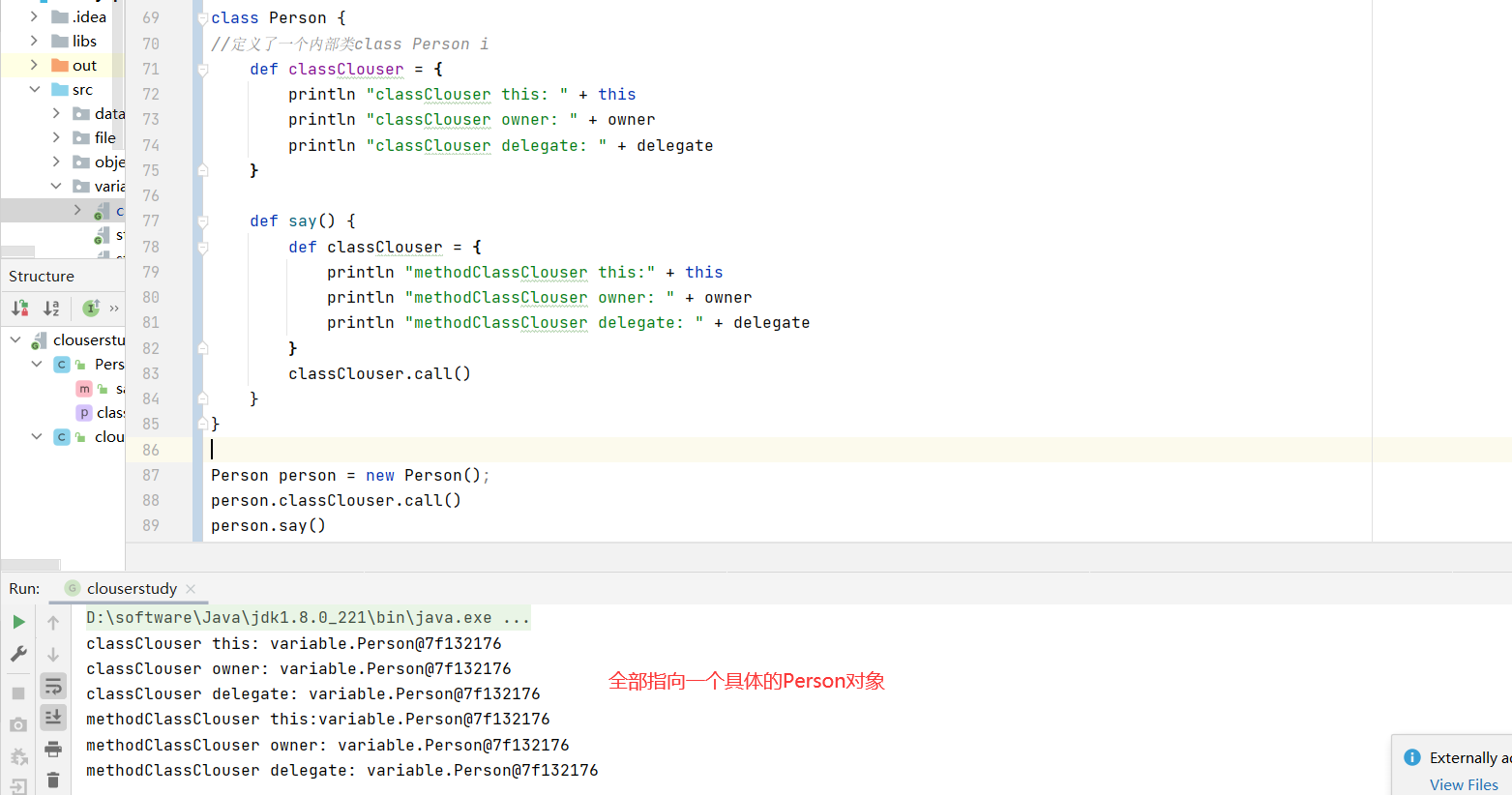
闭包关键变量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def scriptClouser = { println "scriptClouser this: " + this println "scriptClouser owner: " + owner println "scriptClouser delegate: " + delegate } scriptClouser.call()
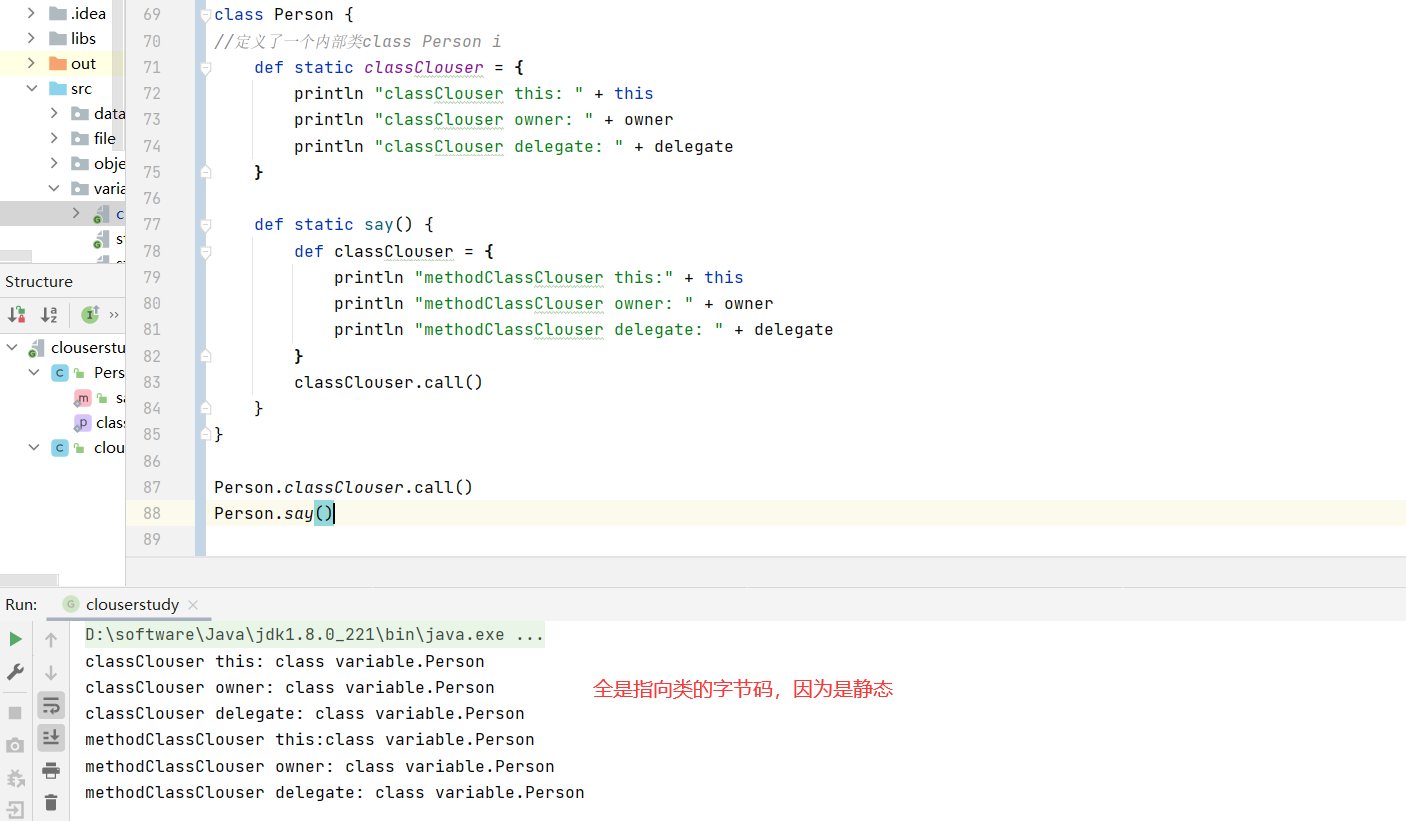
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Person { def static classClouser = { println "classClouser this: " + this println "classClouser owner: " + owner println "classClouser delegate: " + delegate } def static say() { def classClouser = { println "methodClassClouser this:" + this println "methodClassClouser owner: " + owner println "methodClassClouser delegate: " + delegate } classClouser.call() } } Person.classClouser.call() Person.say()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Person { def classClouser = { println "classClouser this: " + this println "classClouser owner: " + owner println "classClouser delegate: " + delegate } def say() { def classClouser = { println "methodClassClouser this:" + this println "methodClassClouser owner: " + owner println "methodClassClouser delegate: " + delegate } classClouser.call() } } Person person = new Person(); person.classClouser.call() person.say()
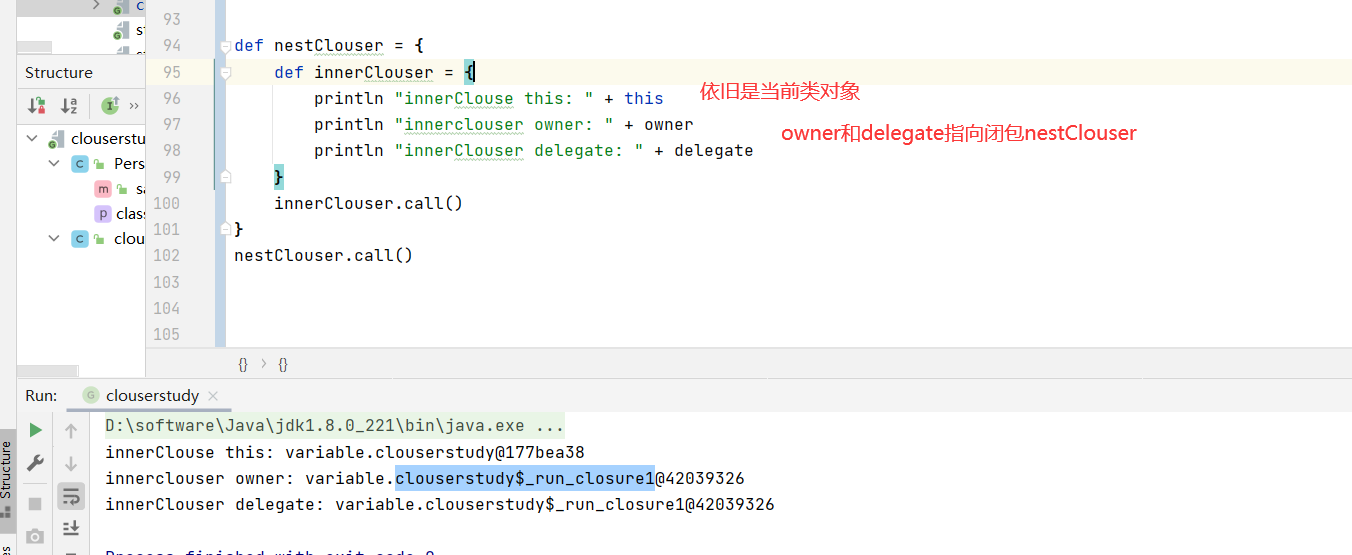
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def nestClouser = { def innerClouser = { println "innerClouse this: " + this println "innerclouser owner: " + owner println "innerClouser delegate: " + delegate } innerClouser.call() } nestClouser.call()
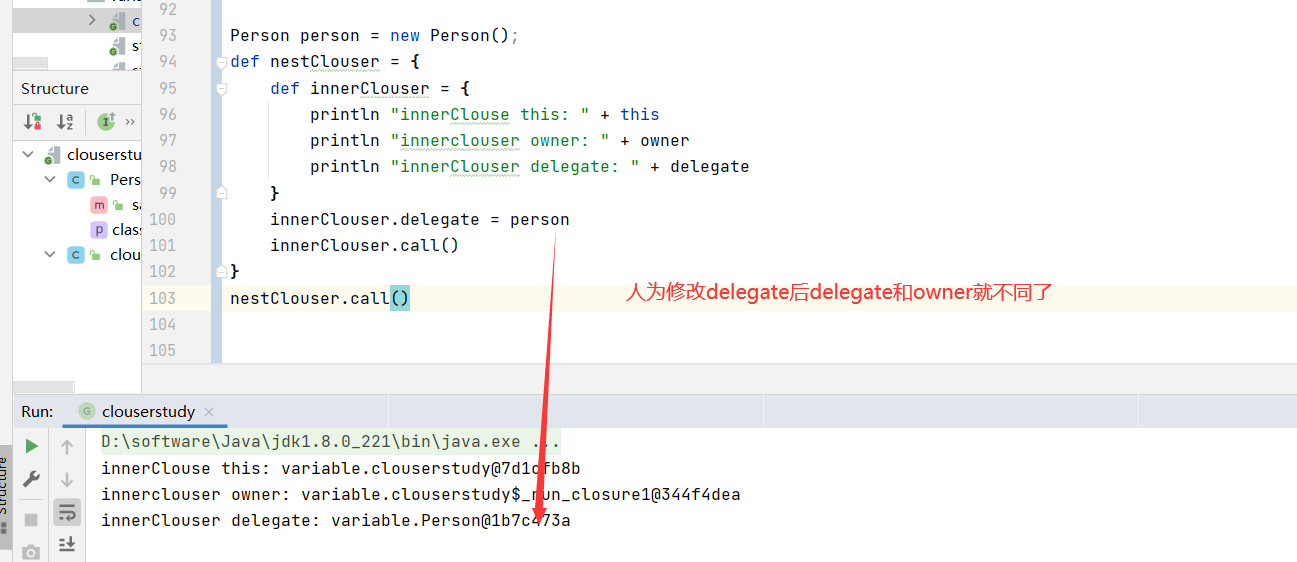
人为修改delegate(this和 owner是不可以修改的)
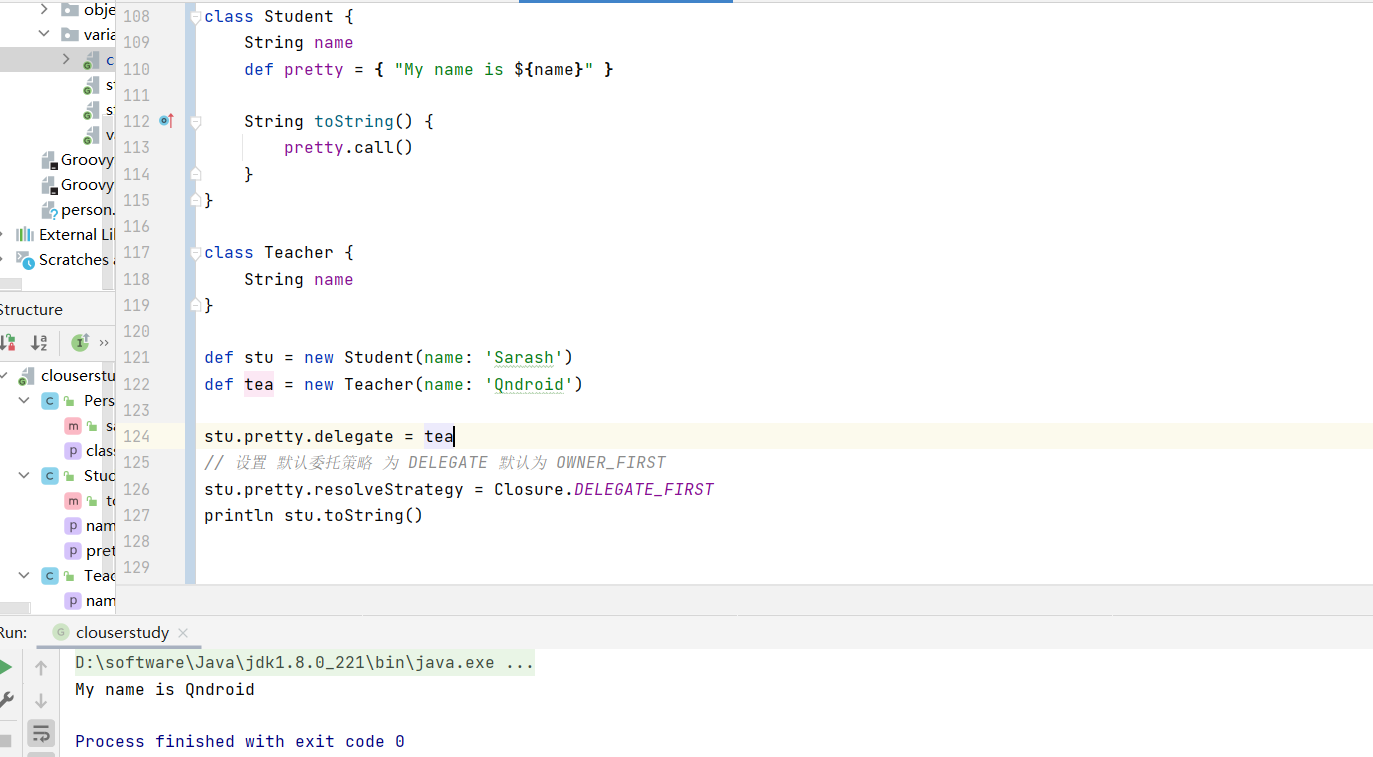
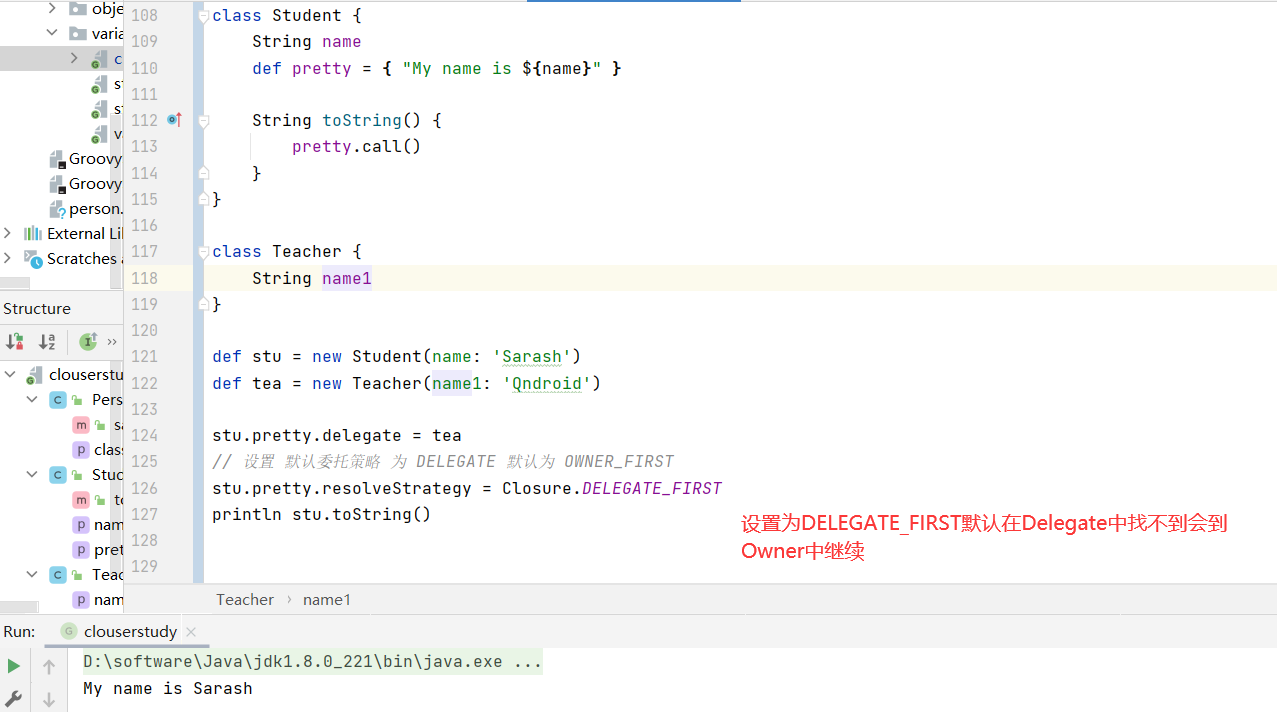
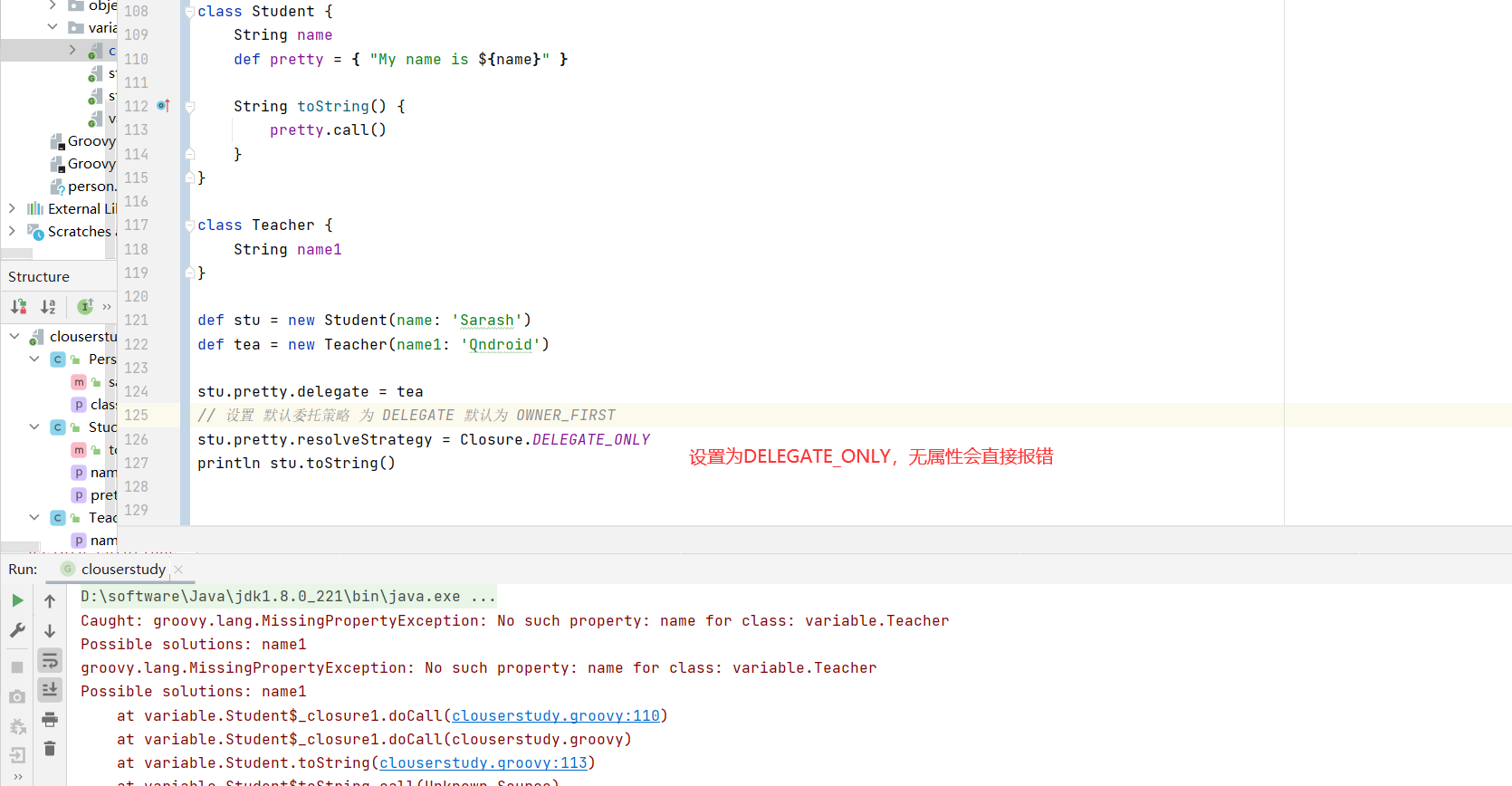
闭包委托策略 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Student { String name def pretty = { "My name is ${name}" } String toString() { pretty.call() } } class Teacher { String name } def stu = new Student(name: 'Sarash' )def tea = new Teacher(name: 'Qndroid' )println stu.toString()
现在想让输出 toString 打印 出 name 为 Qndroid
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Student { String name def pretty = { "My name is ${name}" } String toString() { pretty.call() } } class Teacher { String name } def stu = new Student(name: 'Sarash' )def tea = new Teacher(name: 'Qndroid' )stu.pretty.delegate = tea stu.pretty.resolveStrategy = Closure.DELEGATE_FIRST println stu.toString()
与数据结构结合使用 与文件等结合使用
groovy数据结构 groovy中列表详解 列表的定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def list = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]println list.class println list.size()class def array = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ] as int [] int [] array2 = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
列表添加元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def list = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]list.add(6 ) list.leftShift(7 ) list << 8 println list.toListString() def plusList = list + 9 println plusList.toListString()
列表删除元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 def list = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]list.add(6 ) list.leftShift(7 ) list << 8 list << 9 list << 10 list.remove(7 ) println list.toListString() list.remove((Object) 7 ) println list.toListString() list.removeAt(7 ) println list.toListString() list.removeElement(6 ) println list.toListString() list.removeAll { return it % 2 == 0 } println list.toListString() println list - [6 , 7 ] println list.toListString()
列表排序
1 2 def sortList = [6 , -3 , 9 , 2 , -7 , 1 , 5 ]Collections.sort(sortList)
1 2 3 4 5 Comparator mc = { a, b -> a == b ? 0 : Math.abs(a) < Math.abs(b) ? -1 : 1 } Collections.sort(sortList, mc)
1 2 3 4 5 sortList.sort { a, b -> a == b ? 0 : Math.abs(a) < Math.abs(b) ? 1 : -1 } println sortList
1 2 3 def sortStringList = ['abc' , 'z' , 'Hello' , 'groovy' , 'java' ]sortStringList.sort { it -> return it.size() } println sortStringList
列表查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def findList = [-3 , 9 , 6 , 2 , -7 , 1 , 5 ]println findList.find { return it % 2 == 0 } println findList.findAll { return it % 2 != 0 } println findList.any { return it % 2 != 0 } println findList.every { it % 2 == 0 } println findList.min { return Math.abs(it) } println findList.max { return Math.abs(it) } println findList.count { return it % 2 == 0 }
groovy中的映射详解 定义,访问,添加元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package datastructdef colors = [red : 'ff0000' , green: '00ff00' , blue : '0000ff' ] println colors.getAt('red' ) println colors['red' ] println colors.red colors.yellow = 'ffff00' colors.complex = [a: 1 , b: 2 ] println colors.getClass()
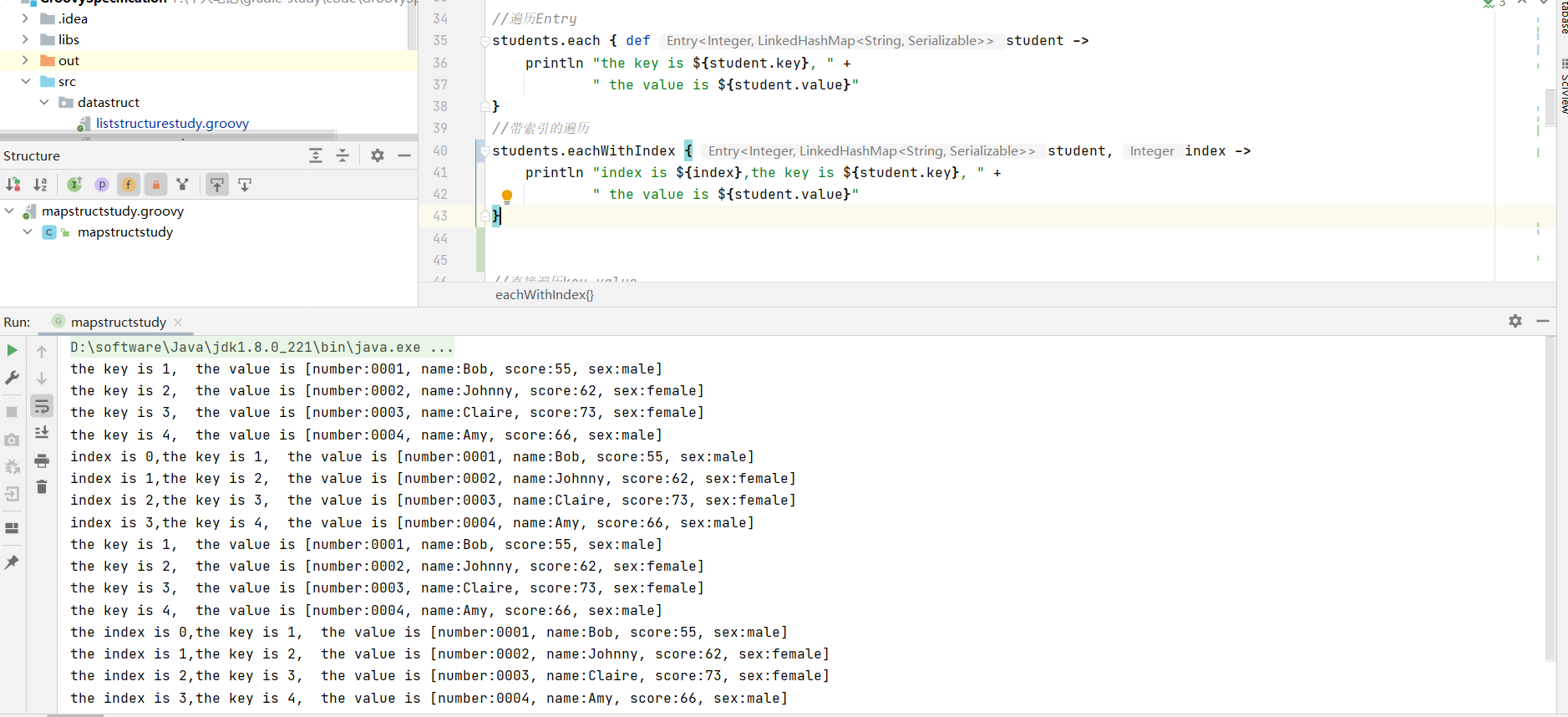
遍历元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 students.each { def student -> println "the key is ${student.key}, " + " the value is ${student.value}" } students.eachWithIndex { student, index -> println "index is ${index},the key is ${student.key}, " + " the value is ${student.value}" } students.each { key, value -> println "the key is ${key}, " + " the value is ${value}" } students.eachWithIndex { key, value, index -> println "the index is ${index},the key is ${key}, " + " the value is ${value}" }
Map的查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 def students = [ 1: [number: '0001' , name: 'Bob' , score : 55 , sex: 'male' ], 2: [number: '0002' , name: 'Johnny' , score : 62 , sex: 'female' ], 3: [number: '0003' , name: 'Claire' , score : 73 , sex: 'female' ], 4: [number: '0004' , name: 'Amy' , score : 66 , sex: 'male' ] ] def entry = students.find { def student -> return student.value.score >= 60 } println entry def entrys = students.findAll { def student -> return student.value.score >= 60 } println entrys def count = students.count { student -> student.value.score >= 60 && student.value.sex == 'male' } println count
Collect收集 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def names = students.findAll { def student -> return student.value.score >= 60 }.collect { return it.value.name } println names.toListString()
group分组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def group = students.groupBy { def student -> return student.value.score >= 60 ? '及格' : '不及格' } println group.toMapString()
排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def sort = students.sort { def student1, def student2 -> Number score1 = student1.value.score Number score2 = student2.value.score return score1 == score2 ? 0 : score1 < score2 ? -1 : 1 } println sort.toMapString() [1 :[number: 0001 , name: Bob, score: 55 , sex: male], 2 :[number: 0002 , name: Johnny, score: 62 , sex: female], 4 :[number: 0004 , name: Amy, score: 66 , sex: male], 3 :[number: 0003 , name: Claire, score: 73 , sex: female]]
groovy中的范围详解 定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package datastructdef range = 1. .10 println range[0 ] println range.contains(10 ) println range.from println range.to
遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 range.each { println it } for (i in range) { println i }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 def result = getGrade(75 )println result def getGrade(Number number) { def result switch (number) { case 0. .<60 : result = '不及格' break case 60. .<70 : result = '及格' break case 70. .<80 : result = '良好' break case 80. .100 : result = '优秀' break } return result }
groovy面向对象 groovy中类,接口等的定义和使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Person implements Serializable { String name Integer age def increaseAge(Integer years) { this .age += years } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package objectorentiondef person = new Person(name: 'Qndroid' , age: 26 )println person.age println person.name println "the name is ${person.getName()},the age is ${person.getAge()}" println person.increaseAge(10 )
Groovy中接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 interface Action { void eat() void drink() void play() }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Person implements Action { String name Integer age def increaseAge(Integer years) { this .age += years } @Override void eat() { } @Override void drink() { } @Override void play() { } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 trait DefualtAction { abstract void eat() void play() { println ' i can play.' } }
Person实现 DefualtAction 只需要重写eat方法即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Person implements DefualtAction { String name Integer age def increaseAge(Integer years) { this .age += years } @Override void eat() { }
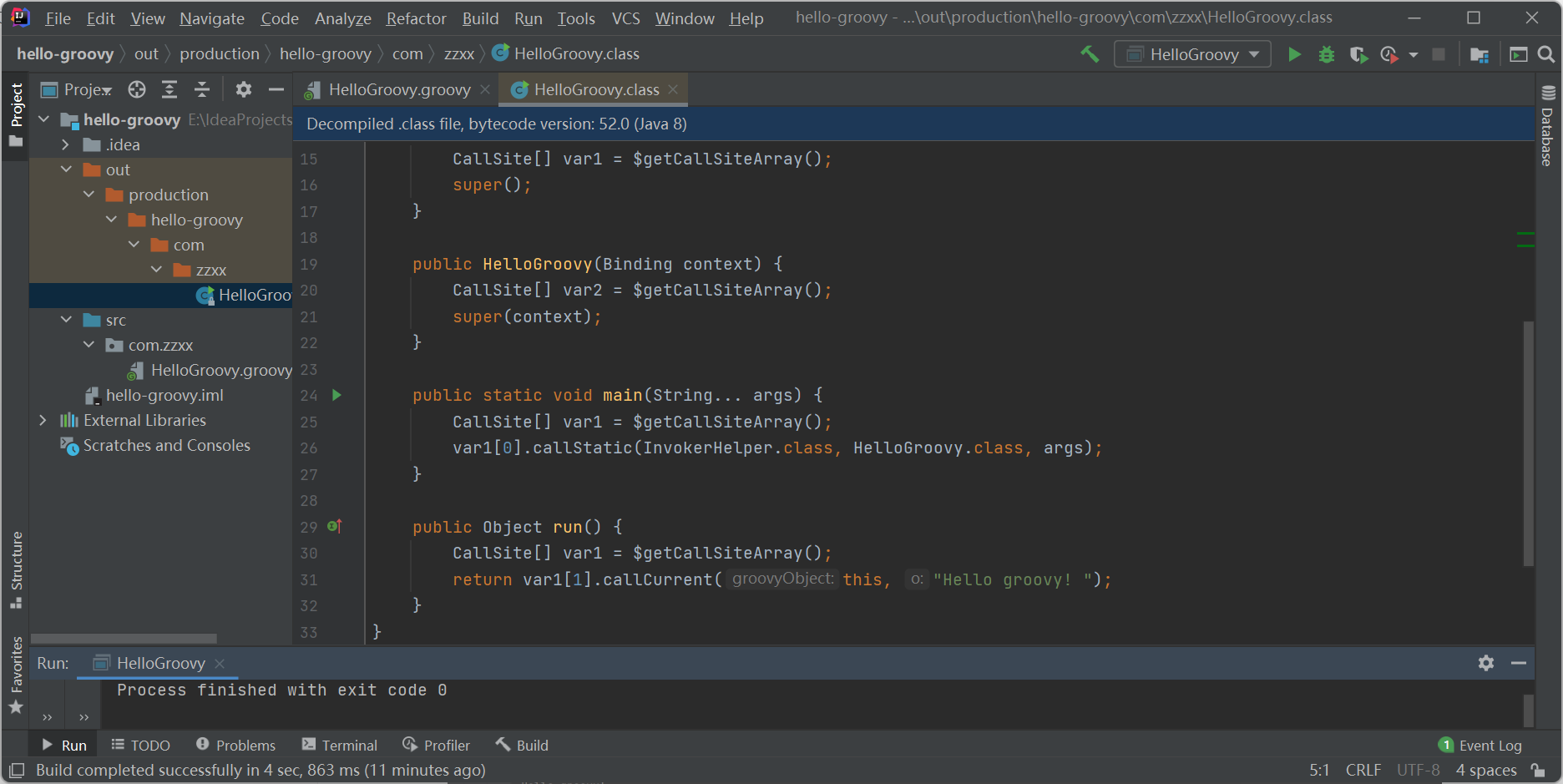
groovy中的元编程 什么是元编程,简单理解 即编写代码执行的时期,有解释执行的js,编译执行的Java,运行时期执行的代码,譬如Java中的反射。
本小节主要是groovy中 运行时期执行的代码 专业术语 runtime
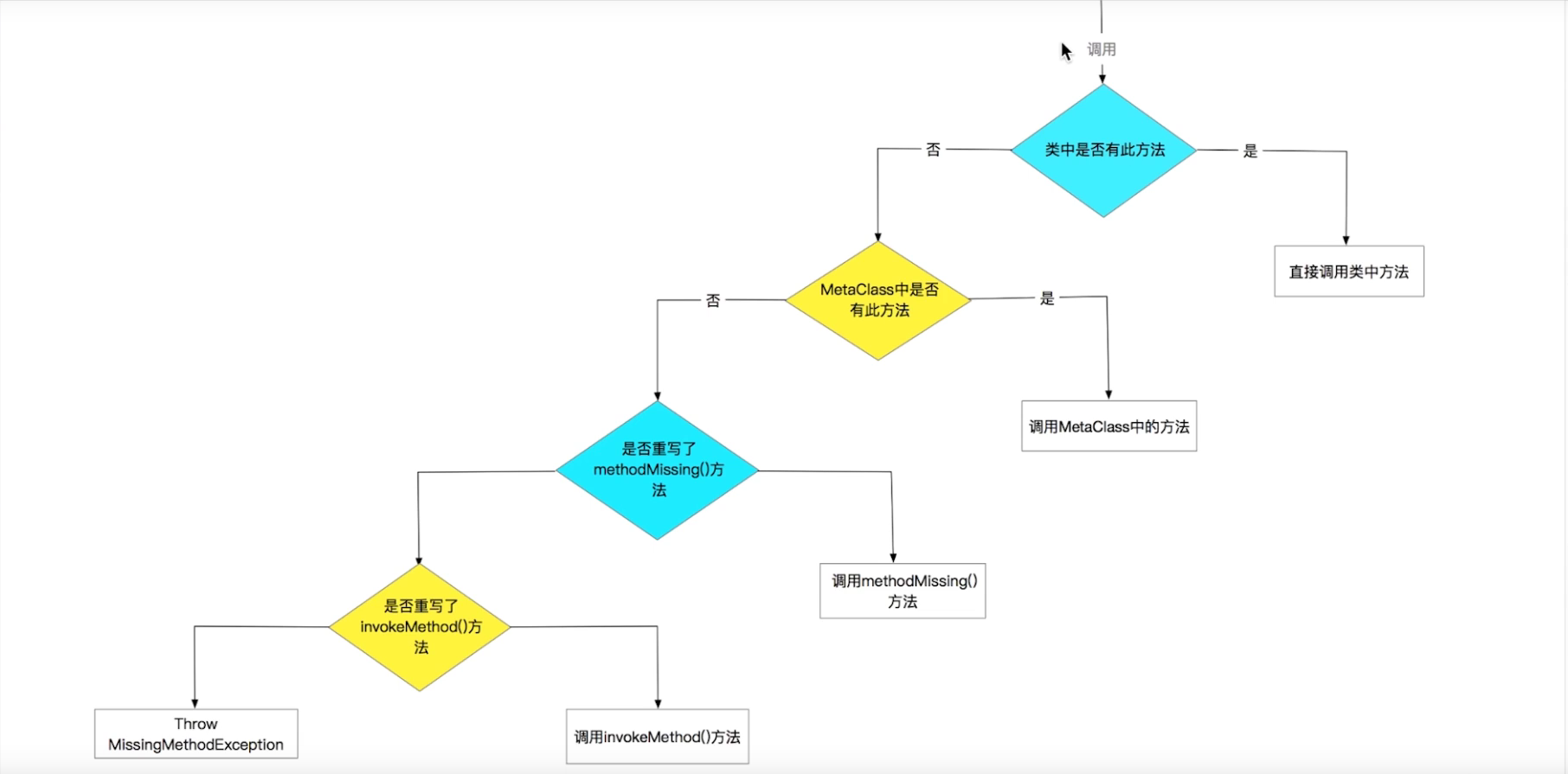
groovy运行期的能力图
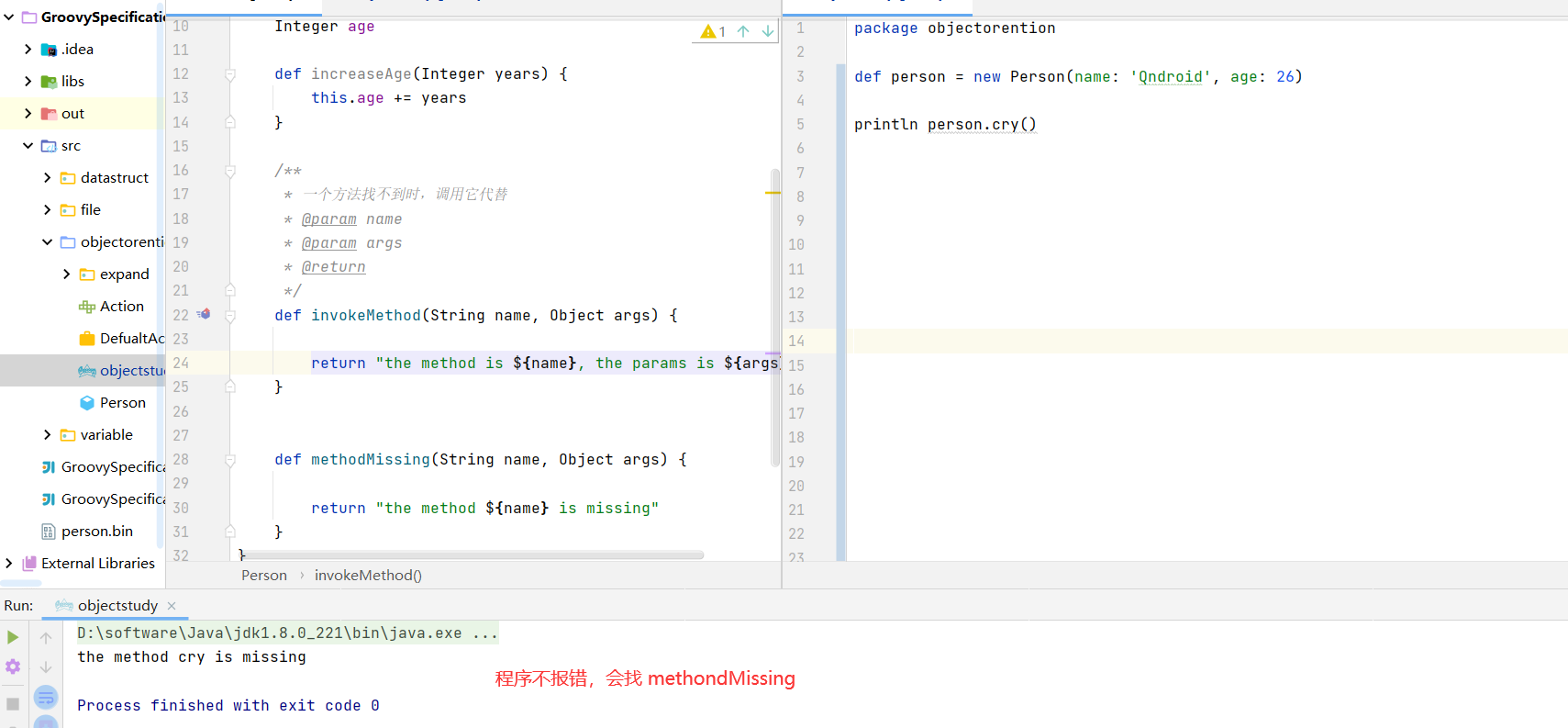
Java中调用方法没有该方法会直接编译不通过
Groovy中没有该方法 类也是可以通过编译的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package objectorentionclass Person implements Serializable { String name Integer age def increaseAge(Integer years) { this .age += years } def invokeMethod(String name, Object args) { return "the method is ${name}, the params is ${args}" } def methodMissing(String name, Object args) { return "the method ${name} is missing" } }
1 2 3 4 package objectorentiondef person = new Person(name: 'Qndroid' , age: 26 )println person.cry()
为类动态的添加一个属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 Person.metaClass.sex = 'male' def person = new Person(name: 'Qndroid' , age: 26 )println person.sex person.sex = 'female' println "the new sex is:" + person.sex
为类动态的添加方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 Person.metaClass.sex = 'male' Person.metaClass.sexUpperCase = { -> sex.toUpperCase() } def person2 = new Person(name: 'Qndroid' , age: 26 )println person2.sexUpperCase()
为类动态的添加静态方法 1 2 3 4 5 Person.metaClass.static .createPerson = { String name, int age -> new Person(name: name, age: age) } def person3 = Person.createPerson('zzxx' , 26 )println person3.name + " and " + person3.age
1 ExpandoMetaClass.enableGlobally()
必知必会
对groovy整体语法特点有一个了解
掌握groovy的变量,字符串,数据结构的用法
掌握groovy的闭包和面向对象思想
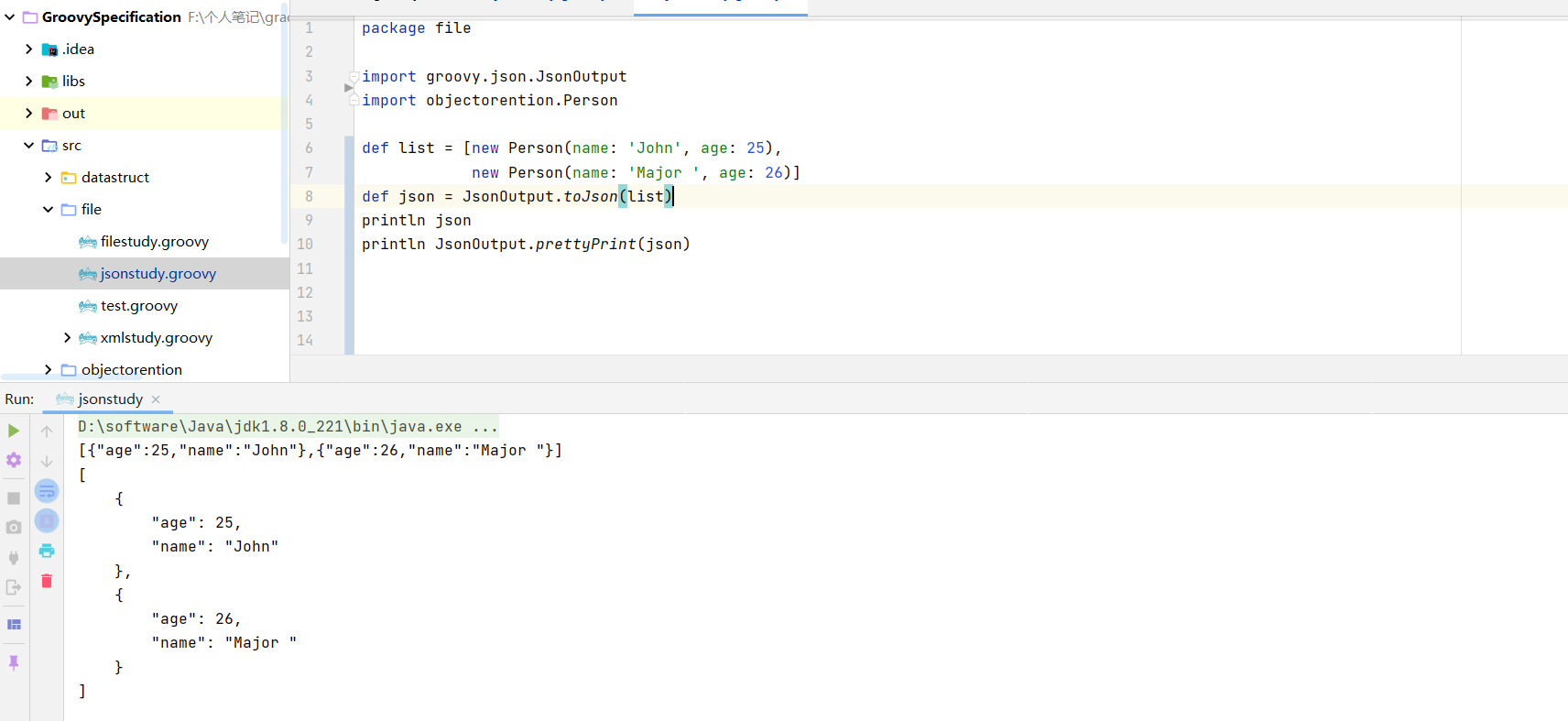
3. Groovy高级用法实战 3.1 JSON操作详解 转JSON字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package fileimport groovy.json.JsonOutputimport objectorention.Persondef list = [new Person(name: 'John' , age: 25 ), new Person(name: 'Major ' , age: 26 )] def json = JsonOutput.toJson(list)println json println JsonOutput.prettyPrint(json)
解析JSON字符串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import groovy.json.JsonOutputimport groovy.json.JsonSlurperimport objectorention.Persondef list = [new Person(name: 'John' , age: 25 ), new Person(name: 'Major ' , age: 26 )] def json = JsonOutput.toJson(list)def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurper();println jsonSlurper.parse(json.getBytes())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 def reponse = getNetworkData('http://yuexibo.top/yxbApp/course_detail.json' )println reponse.data.head.name def getNetworkData(String url) { def connection = new URL(url).openConnection() connection.setRequestMethod('GET' ) connection.connect() def response = connection.content.text def jsonSluper = new JsonSlurper() return jsonSluper.parseText(response) }
3.2 XML操作详解 如何解析一个xml格式数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 final String xml = ''' <response version-api="2.0"> <value> <books id="1" classification="android"> <book available="20" id="1"> <title>疯狂Android讲义</title> <author id="1">李刚</author> </book> <book available="14" id="2"> <title>第一行代码</title> <author id="2">郭林</author> </book> <book available="13" id="3"> <title>Android开发艺术探索</title> <author id="3">任玉刚</author> </book> <book available="5" id="4"> <title>Android源码设计模式</title> <author id="4">何红辉</author> </book> </books> <books id="2" classification="web"> <book available="10" id="1"> <title>Vue从入门到精通</title> <author id="4">李刚</author> </book> </books> </value> </response> '''
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def xmlSluper = new XmlSlurper()def response = xmlSluper.parseText(xml)println response.value.books[0 ].book[0 ].title.text() println response.value.books[0 ].book[0 ].author.text() println response.value.books[1 ].book[0 ].@available
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 def xmlSluper = new XmlSlurper()def response = xmlSluper.parseText(xml)def list = []response.value.books.each { books -> books.book.each { book -> def author = book.author.text() if (author.equals('李刚' )) { list.add(book.title.text()) } } } println list.toListString() def titles = response.depthFirst().findAll { book -> return book.author.text() } println titles.toListString() def name = response.value.books.children().findAll { node -> node.name() == 'book' && node.@id == '2' }.collect { node -> return node.title.text() } println name
如何创建一个xml格式数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 def sw = new StringWriter()def xmlBuilder = new MarkupBuilder(sw) xmlBuilder.langs(type: 'current' , count: '3' , mainstream: 'true' ) { language(flavor: 'static' , version: '1.5' ) { age('16' ) } language(flavor: 'dynamic' , version: '1.6' ) { age('10' ) } language(flavor: 'dynamic' , version: '1.9' , 'JavaScript' ) } println sw def langs = new Langs()xmlBuilder.langs(type: langs.type, count: langs.count, mainstream: langs.mainstream) { langs.languages.each { lang -> language(flavor: lang.flavor, version: lang.version, lang.value) } } class Langs { String type = 'current' int count = 3 boolean mainstream = true def languages = [ new Language(flavor: 'static' , version: '1.5' , value: 'Java' ), new Language(flavor: 'dynamic' , version: '1.3' , value: 'Groovy' ), new Language(flavor: 'dynamic' , version: '1.6' , value: 'JavaScript' ) ] } class Language { String flavor String version String value }
3.3 文件操作
java文件处理
节点流,InputStream, OutputStream及其子类
处理流,Reader,Writer及其子类
读取文件
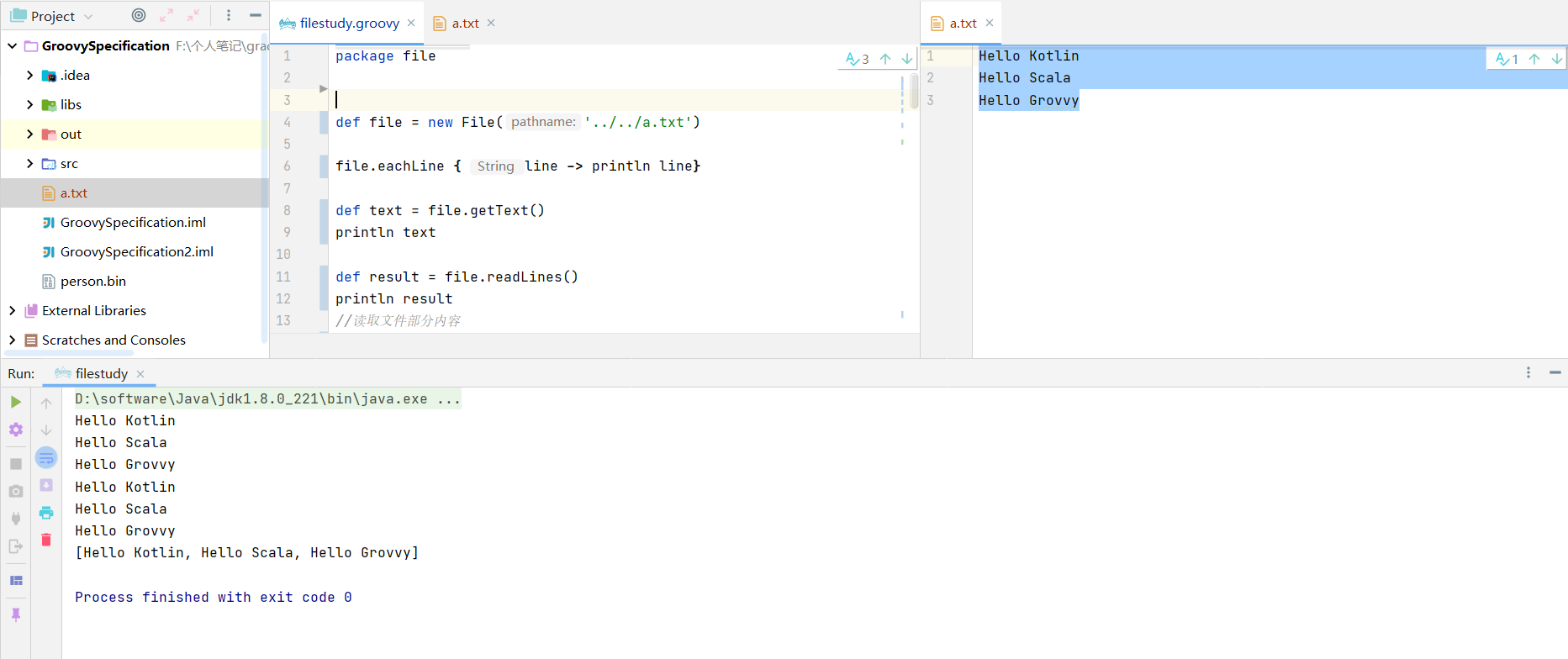
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def file = new File('../../a.txt' )file.eachLine { line -> println line} def text = file.getText()println text def result = file.readLines()println result
1 2 3 4 5 6 def reader = file.withReader { reader -> char [] buffer = new char [10 ] reader.read(buffer) return buffer } println reader
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 def result = copy('../../a.txt' , '../../b.txt' )println result def copy(String sourcePath, String destationPath) { try { def desFile = new File(destationPath) if (!desFile.exists()) { desFile.createNewFile() } new File(sourcePath).withReader { reader -> def lines = reader.readLines() desFile.withWriter { writer -> lines.each { line -> writer.append(line + "\r\n" ) } } } return true } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace() } return false }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package objectorentionclass Person implements Serializable { String name Integer age def increaseAge(Integer years) { this .age += years } def invokeMethod(String name, Object args) { return "the method is ${name}, the params is ${args}" } def methodMissing(String name, Object args) { return "the method ${name} is missing" } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 def person = new Person(name: 'Qndroid' , age: 26 )saveObject(person, '../../person.bin' ) def result = (Person) readObject('../../person.bin' )println "the name is ${result.name} and the age is ${result.age}" def saveObject(Object object, String path) { try { def desFile = new File(path) if (!desFile.exists()) { desFile.createNewFile() } desFile.withObjectOutputStream { out -> out.writeObject(object) } return true } catch (Exception e) { } return false } def readObject(String path) { def obj = null try { def file = new File(path) if (file == null || !file.exists()) return null file.withObjectInputStream { input -> obj = input.readObject() } } catch (Exception e) { } return obj }
groovy与java对比
写法上:没有java那么多的限制
功能上:对java已有的功能进行了极大的扩展
作用上:即可以编写应用,也可以编写脚本
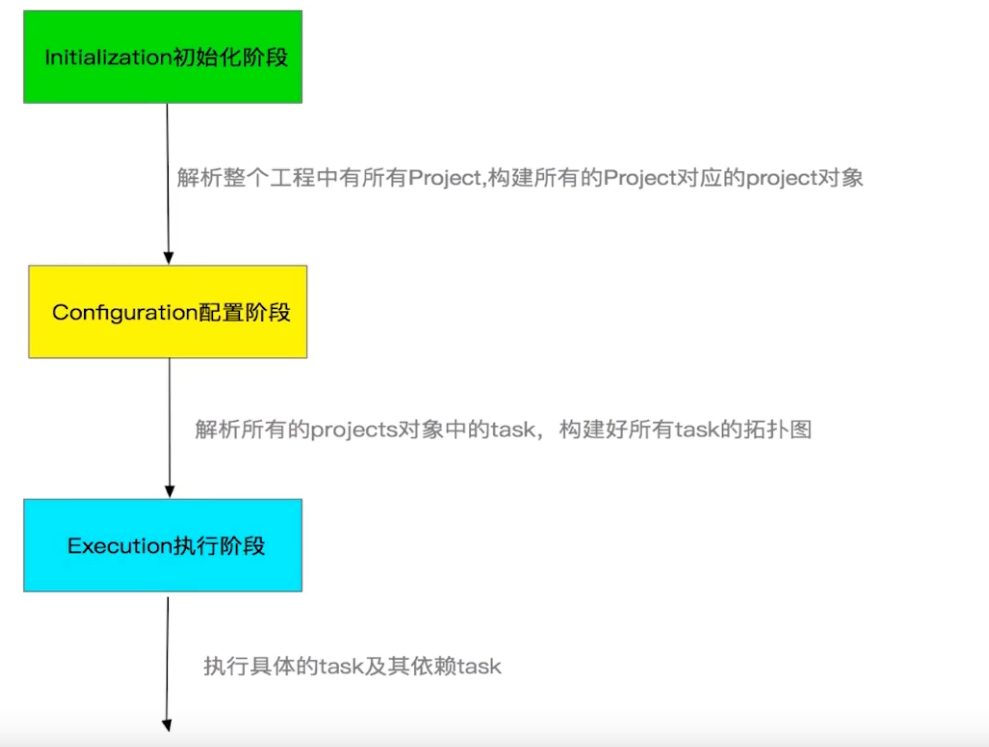
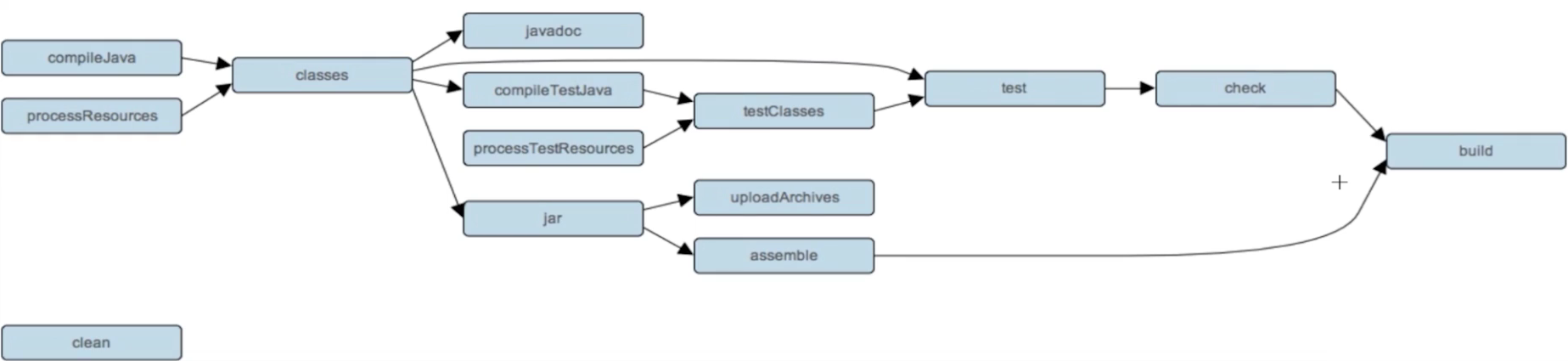
4. Gradle生命周期探索 4.1 gradle基本概念
如果把gradle仅仅看作一个构建工具,那么Gradle的功能就被大大局限了,Gradle更可以被看作编程框架
Gradle有自己的语法(Groovy)又有自己的Api,所以可以被看作编程框架
通过编程实现构建需求是Gradle最大的特色,也是Gradle的核心
gradle组成
groovy核心语法
build script block
gradle api
灵活性上
粒度性上
扩展性上
兼容性上
Gradle核心之Project详解及实战 深入了解Project Project核心API讲解 Project核心API实战